Cholesterol Conjugates of Small Interfering RNA: Linkers and Patterns of Modification
- PMID: 38398538
- PMCID: PMC10892548
- DOI: 10.3390/molecules29040786
Cholesterol Conjugates of Small Interfering RNA: Linkers and Patterns of Modification
Abstract
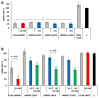
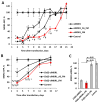
Cholesterol siRNA conjugates attract attention because they allow the delivery of siRNA into cells without the use of transfection agents. In this study, we compared the efficacy and duration of silencing induced by cholesterol conjugates of selectively and totally modified siRNAs and their heteroduplexes of the same sequence and explored the impact of linker length between the 3' end of the sense strand of siRNA and cholesterol on the silencing activity of "light" and "heavy" modified siRNAs. All 3'-cholesterol conjugates were equally active under transfection, but the conjugate with a C3 linker was less active than those with longer linkers (C8 and C15) in a carrier-free mode. At the same time, they were significantly inferior in activity to the 5'-cholesterol conjugate. Shortening the sense strand carrying cholesterol by two nucleotides from the 3'-end did not have a significant effect on the activity of the conjugate. Replacing the antisense strand or both strands with fully modified ones had a significant effect on silencing as well as improving the duration in transfection-mediated and carrier-free modes. A significant 78% suppression of MDR1 gene expression in KB-8-5 xenograft tumors developed in mice promises an advantage from the use of fully modified siRNA cholesterol conjugates in combination chemotherapy.
Keywords: MDR1 gene; chemical modifications; cholesterol conjugate; duration of silencing; nuclease resistance; siRNA.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Structure Tuning of Cationic Oligospermine-siRNA Conjugates for Carrier-Free Gene Silencing.Mol Pharm. 2016 Aug 1;13(8):2718-28. doi: 10.1021/acs.molpharmaceut.6b00309. Epub 2016 Jul 20. Mol Pharm. 2016. PMID: 27398779
-
Trimeric Small Interfering RNAs and Their Cholesterol-Containing Conjugates Exhibit Improved Accumulation in Tumors, but Dramatically Reduced Silencing Activity.Molecules. 2020 Apr 18;25(8):1877. doi: 10.3390/molecules25081877. Molecules. 2020. PMID: 32325757 Free PMC article.
-
Carrier-free cellular uptake and the gene-silencing activity of the lipophilic siRNAs is strongly affected by the length of the linker between siRNA and lipophilic group.Nucleic Acids Res. 2012 Mar;40(5):2330-44. doi: 10.1093/nar/gkr1002. Epub 2011 Nov 10. Nucleic Acids Res. 2012. PMID: 22080508 Free PMC article.
-
Strategies for in vivo delivery of siRNAs: recent progress.BioDrugs. 2010 Jun;24(3):195-205. doi: 10.2165/11534450-000000000-00000. BioDrugs. 2010. PMID: 20462284 Review.
-
Chemical modification of siRNA.Curr Protoc Nucleic Acid Chem. 2009 Dec;Chapter 16:Unit 16.3. doi: 10.1002/0471142700.nc1603s39. Curr Protoc Nucleic Acid Chem. 2009. PMID: 20013783 Review.
Cited by
-
piRNA28846 has the potential to be a novel RNA nucleic acid drug for ovarian cancer.NPJ Precis Oncol. 2025 Mar 8;9(1):65. doi: 10.1038/s41698-025-00840-w. NPJ Precis Oncol. 2025. PMID: 40057617 Free PMC article.
-
Extracellular vesicle mimetics as delivery vehicles for oligonucleotide-based therapeutics and plasmid DNA.Front Bioeng Biotechnol. 2024 Oct 17;12:1437817. doi: 10.3389/fbioe.2024.1437817. eCollection 2024. Front Bioeng Biotechnol. 2024. PMID: 39493304 Free PMC article.
References
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

