Fluacrypyrim Protects Hematopoietic Stem and Progenitor Cells against Irradiation via Apoptosis Prevention
- PMID: 38398568
- PMCID: PMC10893289
- DOI: 10.3390/molecules29040816
Fluacrypyrim Protects Hematopoietic Stem and Progenitor Cells against Irradiation via Apoptosis Prevention
Abstract
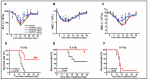
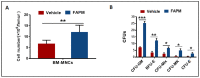
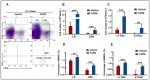
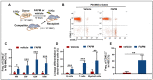
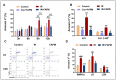
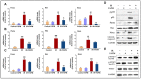
Ionizing radiation (IR)-induced hematopoietic injury has become a global concern in the past decade. The underlying cause of this condition is a compromised hematopoietic reserve, and this kind of hematopoietic injury could result in infection or bleeding, in addition to lethal mishaps. Therefore, developing an effective treatment for this condition is imperative. Fluacrypyrim (FAPM) is a recognized effective inhibitor of STAT3, which exhibits anti-inflammation and anti-tumor effects in hematopoietic disorders. In this context, the present study aimed to determine whether FAPM could serve as a curative agent in hematopoietic-acute radiation syndrome (H-ARS) after total body irradiation (TBI). The results revealed that the peritoneally injection of FAPM could effectively promote mice survival after lethal dose irradiation. In addition, promising recovery of peripheral blood, bone marrow (BM) cell counts, hematopoietic stem cell (HSC) cellularity, BM colony-forming ability, and HSC reconstituting ability upon FAPM treatment after sublethal dose irradiation was noted. Furthermore, FAPM could reduce IR-induced apoptosis in hematopoietic stem and progenitor cells (HSPCs) both in vitro and in vivo. Specifically, FAPM could downregulate the expressions of p53-PUMA pathway target genes, such as Puma, Bax, and Noxa. These results suggested that FAPM played a protective role in IR-induced hematopoietic damage and that the possible underlying mechanism was the modulation of apoptotic activities in HSCs.
Keywords: Fluacrypyrim; apoptosis; hematopoietic stem cells; ionizing radiation; p53-PUMA signaling.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Single-Dose Administration of Recombinant Human Thrombopoietin Mitigates Total Body Irradiation-Induced Hematopoietic System Injury in Mice and Nonhuman Primates.Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys. 2020 Dec 1;108(5):1357-1367. doi: 10.1016/j.ijrobp.2020.07.2325. Epub 2020 Aug 3. Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys. 2020. PMID: 32758640
-
Interleukin-33 regulates hematopoietic stem cell regeneration after radiation injury.Stem Cell Res Ther. 2019 Apr 18;10(1):123. doi: 10.1186/s13287-019-1221-1. Stem Cell Res Ther. 2019. PMID: 30999922 Free PMC article.
-
28Si total body irradiation injures bone marrow hematopoietic stem cells via induction of cellular apoptosis.Life Sci Space Res (Amst). 2017 May;13:39-44. doi: 10.1016/j.lssr.2017.03.003. Epub 2017 Apr 5. Life Sci Space Res (Amst). 2017. PMID: 28554508 Free PMC article.
-
Fluacrypyrim, a novel STAT3 activation inhibitor, induces cell cycle arrest and apoptosis in cancer cells harboring constitutively-active STAT3.Int J Cancer. 2010 Sep 1;127(6):1259-70. doi: 10.1002/ijc.25169. Int J Cancer. 2010. PMID: 20087863
-
Hematopoietic stem cell injury induced by ionizing radiation.Antioxid Redox Signal. 2014 Mar 20;20(9):1447-62. doi: 10.1089/ars.2013.5635. Epub 2014 Feb 10. Antioxid Redox Signal. 2014. PMID: 24124731 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Programmed cell death regulates hematopoietic cell homeostasis under radiation conditions.Stem Cell Res Ther. 2025 Jul 21;16(1):390. doi: 10.1186/s13287-025-04502-3. Stem Cell Res Ther. 2025. PMID: 40691803 Free PMC article.
References
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

