The Promising Role of Polyphenols in Skin Disorders
- PMID: 38398617
- PMCID: PMC10893284
- DOI: 10.3390/molecules29040865
The Promising Role of Polyphenols in Skin Disorders
Abstract
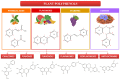
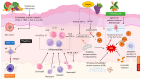
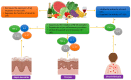
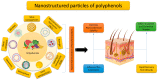
The biochemical characteristics of polyphenols contribute to their numerous advantageous impacts on human health. The existing research suggests that plant phenolics, whether consumed orally or applied directly to the skin, can be beneficial in alleviating symptoms and avoiding the development of many skin disorders. Phenolic compounds, which are both harmless and naturally present, exhibit significant potential in terms of counteracting the effects of skin damage, aging, diseases, wounds, and burns. Moreover, polyphenols play a preventive role and possess the ability to delay the progression of several skin disorders, ranging from small and discomforting to severe and potentially life-threatening ones. This article provides a concise overview of recent research on the potential therapeutic application of polyphenols for skin conditions. It specifically highlights studies that have investigated clinical trials and the use of polyphenol-based nanoformulations for the treatment of different skin ailments.
Keywords: clinical trials; human health; nanoformulations; polyphenols; skin disorder.
Conflict of interest statement
The author declares no conflicts of interest.
Figures

Similar articles
-
The Potential of Plant Phenolics in Prevention and Therapy of Skin Disorders.Int J Mol Sci. 2016 Feb 18;17(2):160. doi: 10.3390/ijms17020160. Int J Mol Sci. 2016. PMID: 26901191 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Plant Polyphenols: Natural and Potent UV-Protective Agents for the Prevention and Treatment of Skin Disorders.Mini Rev Med Chem. 2021;21(5):576-585. doi: 10.2174/1389557520666201109121246. Mini Rev Med Chem. 2021. PMID: 33167833 Review.
-
Exploring Phenolic Compounds in Crop By-Products for Cosmetic Efficacy.Int J Mol Sci. 2024 May 28;25(11):5884. doi: 10.3390/ijms25115884. Int J Mol Sci. 2024. PMID: 38892070 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Polyphenol Conjugates and Human Health: A Perspective Review.Crit Rev Food Sci Nutr. 2016;56(2):326-37. doi: 10.1080/10408398.2012.752342. Crit Rev Food Sci Nutr. 2016. PMID: 24867371 Review.
-
Application of Polyphenols and Flavonoids in Oncological Therapy.Molecules. 2023 May 13;28(10):4080. doi: 10.3390/molecules28104080. Molecules. 2023. PMID: 37241819 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
The state of the art in anti-aging: plant-based phytochemicals for skin care.Immun Ageing. 2025 Jan 31;22(1):5. doi: 10.1186/s12979-025-00498-9. Immun Ageing. 2025. PMID: 39891253 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Soothing the Itch: The Role of Medicinal Plants in Alleviating Pruritus in Palliative Care.Plants (Basel). 2024 Dec 16;13(24):3515. doi: 10.3390/plants13243515. Plants (Basel). 2024. PMID: 39771213 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Phytotherapeutic potential of Campomanesia xanthocarpa (Mart.) O. Berg: antitumor effects in vitro and in silico, with emphasis on SK-MEL-28 melanoma cells-a study on leaf and fruit infusions.In Silico Pharmacol. 2024 Nov 19;12(2):105. doi: 10.1007/s40203-024-00286-1. eCollection 2024. In Silico Pharmacol. 2024. PMID: 39569036
-
Nanoparticle-Encapsulated Plant Polyphenols and Flavonoids as an Enhanced Delivery System for Anti-Acne Therapy.Pharmaceuticals (Basel). 2025 Feb 4;18(2):209. doi: 10.3390/ph18020209. Pharmaceuticals (Basel). 2025. PMID: 40006023 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Harnessing the Power of Polyphenols: A New Frontier in Disease Prevention and Therapy.Pharmaceuticals (Basel). 2024 May 27;17(6):692. doi: 10.3390/ph17060692. Pharmaceuticals (Basel). 2024. PMID: 38931359 Free PMC article. Review.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

