Hybrid Impedimetric Biosensors for Express Protein Markers Detection
- PMID: 38398911
- PMCID: PMC10890403
- DOI: 10.3390/mi15020181
Hybrid Impedimetric Biosensors for Express Protein Markers Detection
Abstract
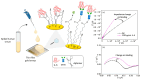
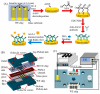
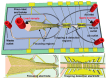
Impedimetric biosensors represent a powerful and promising tool for studying and monitoring biological processes associated with proteins and can contribute to the development of new approaches in the diagnosis and treatment of diseases. The basic principles, analytical methods, and applications of hybrid impedimetric biosensors for express protein detection in biological fluids are described. The advantages of this type of biosensors, such as simplicity and speed of operation, sensitivity and selectivity of analysis, cost-effectiveness, and an ability to be integrated into hybrid microfluidic systems, are demonstrated. Current challenges and development prospects in this area are analyzed. They include (a) the selection of materials for electrodes and formation of nanostructures on their surface; (b) the development of efficient methods for biorecognition elements' deposition on the electrodes' surface, providing the specificity and sensitivity of biosensing; (c) the reducing of nonspecific binding and interference, which could affect specificity; (d) adapting biosensors to real samples and conditions of operation; (e) expanding the range of detected proteins; and, finally, (f) the development of biosensor integration into large microanalytical system technologies. This review could be useful for researchers working in the field of impedimetric biosensors for protein detection, as well as for those interested in the application of this type of biosensor in biomedical diagnostics.
Keywords: antibodies; aptamers; electrochemical impedance spectroscopy; express detection; impedimetric biosensors; label-free detection; microfluidics; nanomaterials; peptides; proteins.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Figures






Similar articles
-
Nanomaterials and Their Recent Applications in Impedimetric Biosensing.Biosensors (Basel). 2023 Sep 22;13(10):899. doi: 10.3390/bios13100899. Biosensors (Basel). 2023. PMID: 37887092 Free PMC article. Review.
-
New trends in impedimetric biosensors for the detection of foodborne pathogenic bacteria.Sensors (Basel). 2012;12(3):3449-71. doi: 10.3390/s120303449. Epub 2012 Mar 12. Sensors (Basel). 2012. PMID: 22737018 Free PMC article. Review.
-
CRISPR-dCas9 powered impedimetric biosensor for label-free detection of circulating tumor DNAs.Anal Chim Acta. 2020 Jul 18;1121:35-41. doi: 10.1016/j.aca.2020.04.009. Epub 2020 Apr 16. Anal Chim Acta. 2020. PMID: 32493587
-
Engineering the bioelectrochemical interface using functional nanomaterials and microchip technique toward sensitive and portable electrochemical biosensors.Biosens Bioelectron. 2016 Feb 15;76:80-90. doi: 10.1016/j.bios.2015.05.037. Epub 2015 May 15. Biosens Bioelectron. 2016. PMID: 26001888 Review.
-
A review on impedimetric biosensors.Artif Cells Nanomed Biotechnol. 2016;44(1):248-62. doi: 10.3109/21691401.2014.942456. Epub 2014 Sep 11. Artif Cells Nanomed Biotechnol. 2016. PMID: 25211230 Review.
Cited by
-
Hybrid-integrated devices for mimicking malignant brain tumors ("tumor-on-a-chip") for in vitro development of targeted drug delivery and personalized therapy approaches.Front Med (Lausanne). 2024 Nov 19;11:1452298. doi: 10.3389/fmed.2024.1452298. eCollection 2024. Front Med (Lausanne). 2024. PMID: 39629230 Free PMC article. Review.
-
A Facile Method for Synthesizing Cobalt Oxide Nanoparticles to Create a Highly Sensitive Non-Enzyme Glucose Sensor.Biosensors (Basel). 2025 Apr 7;15(4):235. doi: 10.3390/bios15040235. Biosensors (Basel). 2025. PMID: 40277548 Free PMC article.
-
Biosensors, Artificial Intelligence Biosensors, False Results and Novel Future Perspectives.Diagnostics (Basel). 2025 Apr 18;15(8):1037. doi: 10.3390/diagnostics15081037. Diagnostics (Basel). 2025. PMID: 40310427 Free PMC article. Review.
References
Publication types
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

