2D Materials Nanoarchitectonics for 3D Structures/Functions
- PMID: 38399187
- PMCID: PMC10890396
- DOI: 10.3390/ma17040936
2D Materials Nanoarchitectonics for 3D Structures/Functions
Abstract
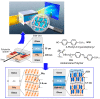
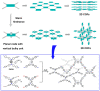
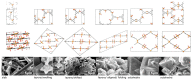
It has become clear that superior material functions are derived from precisely controlled nanostructures. This has been greatly accelerated by the development of nanotechnology. The next step is to assemble materials with knowledge of their nano-level structures. This task is assigned to the post-nanotechnology concept of nanoarchitectonics. However, nanoarchitectonics, which creates intricate three-dimensional functional structures, is not always easy. Two-dimensional nanoarchitectonics based on reactions and arrangements at the surface may be an easier target to tackle. A better methodology would be to define a two-dimensional structure and then develop it into a three-dimensional structure and function. According to these backgrounds, this review paper is organized as follows. The introduction is followed by a summary of the three issues; (i) 2D to 3D dynamic structure control: liquid crystal commanded by the surface, (ii) 2D to 3D rational construction: a metal-organic framework (MOF) and a covalent organic framework (COF); (iii) 2D to 3D functional amplification: cells regulated by the surface. In addition, this review summarizes the important aspects of the ultimate three-dimensional nanoarchitectonics as a perspective. The goal of this paper is to establish an integrated concept of functional material creation by reconsidering various reported cases from the viewpoint of nanoarchitectonics, where nanoarchitectonics can be regarded as a method for everything in materials science.
Keywords: covalent organic framework (COF); liquid crystal; living cell; metal–organic framework (MOF); nanoarchitectonics; surface; three dimensions; two dimensions.
Conflict of interest statement
The author declares no conflict of interest.
Figures


















References
-
- Liu J., Zhang J.-G., Yang Z., Lemmon J.P., Imhoff C., Graff G.L., Li L., Hu J., Wang C., Xiao J., et al. Materials science and materials chemistry for large scale electrochemical energy storage: From transportation to electrical grid. Adv. Funct. Mater. 2013;23:929–946. doi: 10.1002/adfm.201200690. - DOI
-
- Nandihalli N., Liu C.J., Mori T. Polymer based thermoelectric nanocomposite materials and devices: Fabrication and characteristics. Nano Energy. 2020;78:105186. doi: 10.1016/j.nanoen.2020.105186. - DOI
Publication types
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

