A Novel Sandwich-Structured Phase Change Composite with Efficient Photothermal Conversion and Electromagnetic Interference Shielding Interface
- PMID: 38399209
- PMCID: PMC10890597
- DOI: 10.3390/ma17040961
A Novel Sandwich-Structured Phase Change Composite with Efficient Photothermal Conversion and Electromagnetic Interference Shielding Interface
Abstract
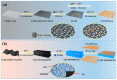
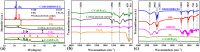
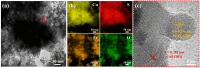
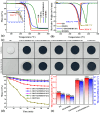
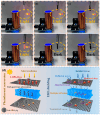
Stability and multifunctionality greatly extend the applications of phase change materials (PCMs) for thermal storage and management. Herein, CuS and Fe3O4 nanoparticles were successfully loaded onto cotton-derived carbon to develop a multifunctional interface with efficient photothermal conversion and electromagnetic interference (EMI) shielding properties. 1,3:2,4-di-(3,4-dimethyl) benzylidene sorbitol (DMDBS) and expanded graphite (EG) formed an organic/inorganic three-dimensional network framework to encapsulate 1-octadecanol (OD) by self-assembly. Finally, multifunctional shape-stabilized PCMs (SSPCMs) with the sandwich structure were prepared by the hot-press process. Multifunctional SSPCMs with high load OD (91%) had favorable thermal storage density (200.6 J/g), thermal stability, and a relatively wider available temperature range with improved thermal conductivity to support the thermal storage and management realization. Furthermore, due to the synergistic enhancement of two nanoparticles and the construction of the carbon network with cotton carbon and EG, highly efficient photothermal conversion (94.4%) and EMI shielding (68.9 dB average, X-band) performance were achieved at about 3 mm thickness, which provided the possibility of the multifunctional integration of PCMs. Conclusively, this study provides new insights towards integrating solar energy utilization with the comprehensive protection of related electronics.
Keywords: electromagnetic interference shielding; multifunctional interfaces; organic composite phase change materials; photothermal conversion; thermal energy storage.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Figures






References
-
- Alawad S.M., Mansour R.B., Al-Sulaiman F.A., Rehman S. Renewable energy systems for water desalination applications: A comprehensive review. Energy Convers. Manag. 2023;286:117035. doi: 10.1016/j.enconman.2023.117035. - DOI
-
- Kumar A., Bhattacharya T., Mukherjee S., Sarkar B. A perspective on biochar for repairing damages in the soil–plant system caused by climate change-driven extreme weather events. Biochar. 2022;4:22. doi: 10.1007/s42773-022-00148-z. - DOI
-
- Kebede A.A., Kalogiannis T., Van Mierlo J., Berecibar M. A comprehensive review of stationary energy storage devices for large scale renewable energy sources grid integration. Renew. Sustain. Energy Rev. 2022;159:112213. doi: 10.1016/j.rser.2022.112213. - DOI
-
- Sikiru S., Oladosu T.L., Amosa T.I., Kolawole S.Y., Soleimani H. Recent advances and impact of phase change materials on solar energy: A comprehensive review. J. Energy Storage. 2022;53:105200. doi: 10.1016/j.est.2022.105200. - DOI
-
- Rathore P.K.S., Gupta N.K., Yadav D., Shukla S.K., Kaul S. Thermal performance of the building envelope integrated with phase change material for thermal energy storage: An updated review. Sustain. Cities Soc. 2022;79:103690. doi: 10.1016/j.scs.2022.103690. - DOI
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

