Applications of Machine Learning (ML) and Mathematical Modeling (MM) in Healthcare with Special Focus on Cancer Prognosis and Anticancer Therapy: Current Status and Challenges
- PMID: 38399314
- PMCID: PMC10892549
- DOI: 10.3390/pharmaceutics16020260
Applications of Machine Learning (ML) and Mathematical Modeling (MM) in Healthcare with Special Focus on Cancer Prognosis and Anticancer Therapy: Current Status and Challenges
Abstract
The use of data-driven high-throughput analytical techniques, which has given rise to computational oncology, is undisputed. The widespread use of machine learning (ML) and mathematical modeling (MM)-based techniques is widely acknowledged. These two approaches have fueled the advancement in cancer research and eventually led to the uptake of telemedicine in cancer care. For diagnostic, prognostic, and treatment purposes concerning different types of cancer research, vast databases of varied information with manifold dimensions are required, and indeed, all this information can only be managed by an automated system developed utilizing ML and MM. In addition, MM is being used to probe the relationship between the pharmacokinetics and pharmacodynamics (PK/PD interactions) of anti-cancer substances to improve cancer treatment, and also to refine the quality of existing treatment models by being incorporated at all steps of research and development related to cancer and in routine patient care. This review will serve as a consolidation of the advancement and benefits of ML and MM techniques with a special focus on the area of cancer prognosis and anticancer therapy, leading to the identification of challenges (data quantity, ethical consideration, and data privacy) which are yet to be fully addressed in current studies.
Keywords: cancer; carcinoma; computational oncology; machine learning; mathematical modeling; telemedicine; tumor.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Figures


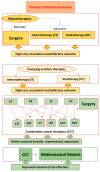
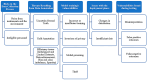
Similar articles
-
The future of Cochrane Neonatal.Early Hum Dev. 2020 Nov;150:105191. doi: 10.1016/j.earlhumdev.2020.105191. Epub 2020 Sep 12. Early Hum Dev. 2020. PMID: 33036834
-
Data-Driven Discovery of Mathematical and Physical Relations in Oncology Data Using Human-Understandable Machine Learning.Front Artif Intell. 2021 Nov 25;4:713690. doi: 10.3389/frai.2021.713690. eCollection 2021. Front Artif Intell. 2021. PMID: 34901835 Free PMC article.
-
A review on utilizing machine learning technology in the fields of electronic emergency triage and patient priority systems in telemedicine: Coherent taxonomy, motivations, open research challenges and recommendations for intelligent future work.Comput Methods Programs Biomed. 2021 Sep;209:106357. doi: 10.1016/j.cmpb.2021.106357. Epub 2021 Aug 16. Comput Methods Programs Biomed. 2021. PMID: 34438223 Review.
-
Data-driven modeling and prediction of blood glucose dynamics: Machine learning applications in type 1 diabetes.Artif Intell Med. 2019 Jul;98:109-134. doi: 10.1016/j.artmed.2019.07.007. Epub 2019 Jul 26. Artif Intell Med. 2019. PMID: 31383477 Review.
-
Machine learning applications in stroke medicine: advancements, challenges, and future prospectives.Neural Regen Res. 2024 Apr;19(4):769-773. doi: 10.4103/1673-5374.382228. Neural Regen Res. 2024. PMID: 37843210 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Machine Learning-Based Morphological Classification and Diversity Analysis of Ornamental Pumpkin Seeds.Foods. 2025 Apr 25;14(9):1498. doi: 10.3390/foods14091498. Foods. 2025. PMID: 40361582 Free PMC article.
-
Overcoming Barriers in Cancer Biology Research: Current Limitations and Solutions.Cancers (Basel). 2025 Jun 23;17(13):2102. doi: 10.3390/cancers17132102. Cancers (Basel). 2025. PMID: 40647400 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Advancing Cancer Drug Delivery with Nanoparticles: Challenges and Prospects in Mathematical Modeling for In Vivo and In Vitro Systems.Cancers (Basel). 2025 Jan 9;17(2):198. doi: 10.3390/cancers17020198. Cancers (Basel). 2025. PMID: 39857980 Free PMC article. Review.
References
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

