Integrating Artificial Intelligence and PET Imaging for Drug Discovery: A Paradigm Shift in Immunotherapy
- PMID: 38399425
- PMCID: PMC10892847
- DOI: 10.3390/ph17020210
Integrating Artificial Intelligence and PET Imaging for Drug Discovery: A Paradigm Shift in Immunotherapy
Abstract
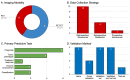
The integration of artificial intelligence (AI) and positron emission tomography (PET) imaging has the potential to become a powerful tool in drug discovery. This review aims to provide an overview of the current state of research and highlight the potential for this alliance to advance pharmaceutical innovation by accelerating the development and deployment of novel therapeutics. We previously performed a scoping review of three databases (Embase, MEDLINE, and CENTRAL), identifying 87 studies published between 2018 and 2022 relevant to medical imaging (e.g., CT, PET, MRI), immunotherapy, artificial intelligence, and radiomics. Herein, we reexamine the previously identified studies, performing a subgroup analysis on articles specifically utilizing AI and PET imaging for drug discovery purposes in immunotherapy-treated oncology patients. Of the 87 original studies identified, 15 met our updated search criteria. In these studies, radiomics features were primarily extracted from PET/CT images in combination (n = 9, 60.0%) rather than PET imaging alone (n = 6, 40.0%), and patient cohorts were mostly recruited retrospectively and from single institutions (n = 10, 66.7%). AI models were used primarily for prognostication (n = 6, 40.0%) or for assisting in tumor phenotyping (n = 4, 26.7%). About half of the studies stress-tested their models using validation sets (n = 4, 26.7%) or both validation sets and test sets (n = 4, 26.7%), while the remaining six studies (40.0%) either performed no validation at all or used less stringent methods such as cross-validation on the training set. Overall, the integration of AI and PET imaging represents a paradigm shift in drug discovery, offering new avenues for more efficient development of therapeutics. By leveraging AI algorithms and PET imaging analysis, researchers could gain deeper insights into disease mechanisms, identify new drug targets, or optimize treatment regimens. However, further research is needed to validate these findings and address challenges such as data standardization and algorithm robustness.
Keywords: PET; PET/CT; artificial intelligence; drug discovery; immunotherapy; radiomics.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Artificial intelligence in immunotherapy PET/SPECT imaging.Eur Radiol. 2024 Sep;34(9):5829-5841. doi: 10.1007/s00330-024-10637-3. Epub 2024 Feb 15. Eur Radiol. 2024. PMID: 38355986 Review.
-
Artificial Intelligence in Breast Cancer: A Systematic Review on PET Imaging Clinical Applications.Curr Med Imaging. 2023;19(8):832-843. doi: 10.2174/1573405619666230126093806. Curr Med Imaging. 2023. PMID: 36703586
-
Artificial Intelligence and Radiomics: Clinical Applications for Patients with Advanced Melanoma Treated with Immunotherapy.Diagnostics (Basel). 2023 Sep 27;13(19):3065. doi: 10.3390/diagnostics13193065. Diagnostics (Basel). 2023. PMID: 37835808 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Advancing precision medicine: the transformative role of artificial intelligence in immunogenomics, radiomics, and pathomics for biomarker discovery and immunotherapy optimization.Cancer Biol Med. 2025 Jan 2;22(1):33-47. doi: 10.20892/j.issn.2095-3941.2024.0376. Cancer Biol Med. 2025. PMID: 39749734 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Artificial intelligence and radiomics: fundamentals, applications, and challenges in immunotherapy.J Immunother Cancer. 2022 Sep;10(9):e005292. doi: 10.1136/jitc-2022-005292. J Immunother Cancer. 2022. PMID: 36180071 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Copper-mediated radiochemistry: historical impact, current trends, and future possibilities.Npj Imaging. 2025 Jun 10;3:25. doi: 10.1038/s44303-025-00087-x. eCollection 2025. Npj Imaging. 2025. PMID: 40510251 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Recent Breakthroughs in PET-CT Multimodality Imaging: Innovations and Clinical Impact.Bioengineering (Basel). 2024 Nov 30;11(12):1213. doi: 10.3390/bioengineering11121213. Bioengineering (Basel). 2024. PMID: 39768032 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Optimizing Cancer Treatment: Exploring the Role of AI in Radioimmunotherapy.Diagnostics (Basel). 2025 Feb 6;15(3):397. doi: 10.3390/diagnostics15030397. Diagnostics (Basel). 2025. PMID: 39941326 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Gastric Emptying Scintigraphy Protocol Optimization Using Machine Learning for the Detection of Delayed Gastric Emptying.Diagnostics (Basel). 2024 Jun 13;14(12):1240. doi: 10.3390/diagnostics14121240. Diagnostics (Basel). 2024. PMID: 38928655 Free PMC article.
-
Synthesis and Anticancer Activity Evaluation of Novel Carborane-Containing Isoflavonoid Analogues.ACS Omega. 2025 Apr 29;10(18):18720-18732. doi: 10.1021/acsomega.5c00262. eCollection 2025 May 13. ACS Omega. 2025. PMID: 40385218 Free PMC article.
References
-
- O’Brien S.G., Guilhot F., Larson R.A., Gathmann I., Baccarani M., Cervantes F., Cornelissen J.J., Fischer T., Hochhaus A., Hughes T., et al. Imatinib Compared with Interferon and Low-Dose Cytarabine for Newly Diagnosed Chronic-Phase Chronic Myeloid Leukemia. N. Engl. J. Med. 2003;348:994–1004. doi: 10.1056/NEJMoa022457. - DOI - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

