Saikosaponin B2, Punicalin, and Punicalagin in Vitro Block Cellular Entry of Feline Herpesvirus-1
- PMID: 38400007
- PMCID: PMC10892935
- DOI: 10.3390/v16020231
Saikosaponin B2, Punicalin, and Punicalagin in Vitro Block Cellular Entry of Feline Herpesvirus-1
Abstract
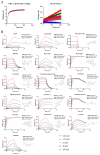
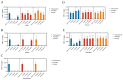
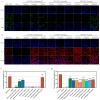
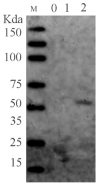
In the realm of clinical practice, nucleoside analogs are the prevailing antiviral drugs employed to combat feline herpesvirus-1 (FHV-1) infections. However, these drugs, initially formulated for herpes simplex virus (HSV) infections, operate through a singular mechanism and are susceptible to the emergence of drug resistance. These challenges underscore the imperative to innovate and develop alternative antiviral medications featuring unique mechanisms of action, such as viral entry inhibitors. This research endeavors to address this pressing need. Utilizing Bio-layer interferometry (BLI), we meticulously screened drugs to identify natural compounds exhibiting high binding affinity for the herpesvirus functional protein envelope glycoprotein B (gB). The selected drugs underwent a rigorous assessment to gauge their antiviral activity against feline herpesvirus-1 (FHV-1) and to elucidate their mode of action. Our findings unequivocally demonstrated that Saikosaponin B2, Punicalin, and Punicalagin displayed robust antiviral efficacy against FHV-1 at concentrations devoid of cytotoxicity. Specifically, these compounds, Saikosaponin B2, Punicalin, and Punicalagin, are effective in exerting their antiviral effects in the early stages of viral infection without compromising the integrity of the viral particle. Considering the potency and efficacy exhibited by Saikosaponin B2, Punicalin, and Punicalagin in impeding the early entry of FHV-1, it is foreseeable that their chemical structures will be further explored and developed as promising antiviral agents against FHV-1 infection.
Keywords: Bio-layer interferometry; envelope glycoprotein B; feline herpesvirus-1; natural compounds; virus entry inhibitor.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Figures


Similar articles
-
A review of antiviral drugs and other compounds with activity against feline herpesvirus type 1.Vet Ophthalmol. 2016 Jul;19 Suppl 1(Suppl 1):119-30. doi: 10.1111/vop.12375. Epub 2016 Apr 19. Vet Ophthalmol. 2016. PMID: 27091747 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Green tea extract reduces viral proliferation and ROS production during Feline Herpesvirus type-1 (FHV-1) infection.BMC Vet Res. 2024 Aug 22;20(1):374. doi: 10.1186/s12917-024-04227-0. BMC Vet Res. 2024. PMID: 39175036 Free PMC article.
-
Antiviral effect of sinefungin on in vitro growth of feline herpesvirus type 1.J Antibiot (Tokyo). 2019 Dec;72(12):981-985. doi: 10.1038/s41429-019-0234-4. Epub 2019 Sep 18. J Antibiot (Tokyo). 2019. PMID: 31534199
-
A novel corneal explant model system to evaluate antiviral drugs against feline herpesvirus type 1 (FHV-1).J Gen Virol. 2016 Jun;97(6):1414-1425. doi: 10.1099/jgv.0.000451. Epub 2016 Mar 9. J Gen Virol. 2016. PMID: 26959283
-
[Treatment of acute viral feline upper respiratory tract infections].Tierarztl Prax Ausg K Kleintiere Heimtiere. 2019 Apr;47(2):98-109. doi: 10.1055/a-0870-0801. Epub 2019 Apr 23. Tierarztl Prax Ausg K Kleintiere Heimtiere. 2019. PMID: 31013527 Review. German.
Cited by
-
Preliminary Data on the Antiviral Activity of Helleborus bocconei subsp. intermedius Root Extracts Against Animal Herpesviruses.Microorganisms. 2025 Apr 12;13(4):891. doi: 10.3390/microorganisms13040891. Microorganisms. 2025. PMID: 40284727 Free PMC article.
-
Alphaherpesvirus in Pets and Livestock.Microorganisms. 2025 Jan 4;13(1):82. doi: 10.3390/microorganisms13010082. Microorganisms. 2025. PMID: 39858850 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The Therapeutic Efficacy and Molecular Mechanisms of Artemisia argyi Essential Oil in Treating Feline Herpesvirus Infection via Nasal Drops.Vet Sci. 2025 Jan 23;12(2):80. doi: 10.3390/vetsci12020080. Vet Sci. 2025. PMID: 40005840 Free PMC article.
References
MeSH terms
Substances
Supplementary concepts
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

