Detection of Rehabilitation Training Effect of Upper Limb Movement Disorder Based on MPL-CNN
- PMID: 38400263
- PMCID: PMC10892837
- DOI: 10.3390/s24041105
Detection of Rehabilitation Training Effect of Upper Limb Movement Disorder Based on MPL-CNN
Abstract
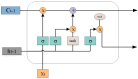
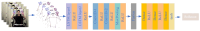
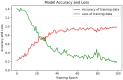
Stroke represents a medical emergency and can lead to the development of movement disorders such as abnormal muscle tone, limited range of motion, or abnormalities in coordination and balance. In order to help stroke patients recover as soon as possible, rehabilitation training methods employ various movement modes such as ordinary movements and joint reactions to induce active reactions in the limbs and gradually restore normal functions. Rehabilitation effect evaluation can help physicians understand the rehabilitation needs of different patients, determine effective treatment methods and strategies, and improve treatment efficiency. In order to achieve real-time and accuracy of action detection, this article uses Mediapipe's action detection algorithm and proposes a model based on MPL-CNN. Mediapipe can be used to identify key point features of the patient's upper limbs and simultaneously identify key point features of the hand. In order to detect the effect of rehabilitation training for upper limb movement disorders, LSTM and CNN are combined to form a new LSTM-CNN model, which is used to identify the action features of upper limb rehabilitation training extracted by Medipipe. The MPL-CNN model can effectively identify the accuracy of rehabilitation movements during upper limb rehabilitation training for stroke patients. In order to ensure the scientific validity and unified standards of rehabilitation training movements, this article employs the postures in the Fugl-Meyer Upper Limb Rehabilitation Training Functional Assessment Form (FMA) and establishes an FMA upper limb rehabilitation data set for experimental verification. Experimental results show that in each stage of the Fugl-Meyer upper limb rehabilitation training evaluation effect detection, the MPL-CNN-based method's recognition accuracy of upper limb rehabilitation training actions reached 95%. At the same time, the average accuracy rate of various upper limb rehabilitation training actions reaches 97.54%. This shows that the model is highly robust across different action categories and proves that the MPL-CNN model is an effective and feasible solution. This method based on MPL-CNN can provide a high-precision detection method for the evaluation of rehabilitation effects of upper limb movement disorders after stroke, helping clinicians in evaluating the patient's rehabilitation progress and adjusting the rehabilitation plan based on the evaluation results. This will help improve the personalization and precision of rehabilitation treatment and promote patient recovery.
Keywords: MPL-CNN; Mediapipe; action recognition; deep learning; rehabilitation assessment.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Figures




Similar articles
-
Construction of efficacious gait and upper limb functional interventions based on brain plasticity evidence and model-based measures for stroke patients.ScientificWorldJournal. 2007 Dec 20;7:2031-45. doi: 10.1100/tsw.2007.299. ScientificWorldJournal. 2007. PMID: 18167618 Free PMC article.
-
Bilateral upper limb training with functional electric stimulation in patients with chronic stroke.Neurorehabil Neural Repair. 2009 May;23(4):357-65. doi: 10.1177/1545968308326428. Epub 2008 Dec 12. Neurorehabil Neural Repair. 2009. PMID: 19074684 Clinical Trial.
-
The contribution of kinematics in the assessment of upper limb motor recovery early after stroke.Neurorehabil Neural Repair. 2014 Jan;28(1):4-12. doi: 10.1177/1545968313498514. Epub 2013 Aug 1. Neurorehabil Neural Repair. 2014. PMID: 23911973
-
Effects of physical therapy-based rehabilitation on recovery of upper limb motor function after stroke in adults: a systematic review and meta-analysis of randomized controlled trials.Ann Palliat Med. 2022 Feb;11(2):521-531. doi: 10.21037/apm-21-3710. Ann Palliat Med. 2022. PMID: 35249330
-
The Effects of Unilateral Versus Bilateral Motor Training on Upper Limb Function in Adults with Chronic Stroke: A Systematic Review.J Stroke Cerebrovasc Dis. 2021 Apr;30(4):105617. doi: 10.1016/j.jstrokecerebrovasdis.2021.105617. Epub 2021 Jan 27. J Stroke Cerebrovasc Dis. 2021. PMID: 33516068
Cited by
-
Optimizing the impact of time domain segmentation techniques on upper limb EMG decoding using multimodal features.PLoS One. 2025 May 8;20(5):e0322580. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0322580. eCollection 2025. PLoS One. 2025. PMID: 40338888 Free PMC article.
-
Influence of wearable rhythmic auditory stimulation on Parkinson's disease, multiple sclerosis, and stroke: a systematic review and meta-analysis.Sci Rep. 2025 Jul 1;15(1):21432. doi: 10.1038/s41598-025-05952-8. Sci Rep. 2025. PMID: 40595956 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Feigin V.L., Brainin M., Norrving B., Martins S., Sacco R.L., Hacke W., Fisher M., Pandian J., Lindsay P. World Stroke Organization (WSO): Global Stroke Fact Sheet 2022. Volume 17. WSO; Singapore: 2022. pp. 18–29. - PubMed
-
- Kwakkel G., Kollen B.J., van der Grond J., Prevo A.J.H., Kollen B., Prevo J. Probability of regaining dexterity in the flaccid upper limb: Impact of severity of paresis and time since onset in acute stroke. Stroke. 2003;34:2181–2186. doi: 10.1161/01.STR.0000087172.16305.CD. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Sammali E., Alia C., Vegliante G., Colombo V., Giordano N., Pischiutta F., Boncoraglio G.B., Barilani M., Lazzari L., Caleo M., et al. Intravenous infusion of human bone marrow mesenchymal stromal cells promotes functional recovery and neuroplasticity after ischemic stroke in mice. Sci. Rep. 2017;7:6962. doi: 10.1038/s41598-017-07274-w. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

