Respiratory Diseases Diagnosis Using Audio Analysis and Artificial Intelligence: A Systematic Review
- PMID: 38400330
- PMCID: PMC10893010
- DOI: 10.3390/s24041173
Respiratory Diseases Diagnosis Using Audio Analysis and Artificial Intelligence: A Systematic Review
Abstract
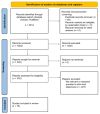
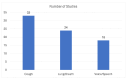
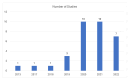
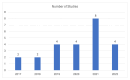
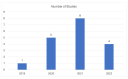
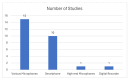
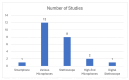
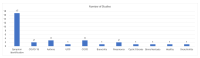
Respiratory diseases represent a significant global burden, necessitating efficient diagnostic methods for timely intervention. Digital biomarkers based on audio, acoustics, and sound from the upper and lower respiratory system, as well as the voice, have emerged as valuable indicators of respiratory functionality. Recent advancements in machine learning (ML) algorithms offer promising avenues for the identification and diagnosis of respiratory diseases through the analysis and processing of such audio-based biomarkers. An ever-increasing number of studies employ ML techniques to extract meaningful information from audio biomarkers. Beyond disease identification, these studies explore diverse aspects such as the recognition of cough sounds amidst environmental noise, the analysis of respiratory sounds to detect respiratory symptoms like wheezes and crackles, as well as the analysis of the voice/speech for the evaluation of human voice abnormalities. To provide a more in-depth analysis, this review examines 75 relevant audio analysis studies across three distinct areas of concern based on respiratory diseases' symptoms: (a) cough detection, (b) lower respiratory symptoms identification, and (c) diagnostics from the voice and speech. Furthermore, publicly available datasets commonly utilized in this domain are presented. It is observed that research trends are influenced by the pandemic, with a surge in studies on COVID-19 diagnosis, mobile data acquisition, and remote diagnosis systems.
Keywords: audio analysis; audio-based biomarkers; digital biomarkers; machine learning; respiratory disease; respiratory symptoms; signal processing; systematic review.
Conflict of interest statement
This research was conducted as a collaboration between the University of Patras in Greece and Pfizer. Pfizer is the research sponsor.
Figures


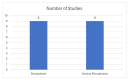
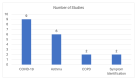
References
-
- Ijaz A., Nabeel M., Masood U., Mahmood T., Hashmi M.S., Posokhova I., Rizwan A., Imran A. Towards using cough for respiratory disease diagnosis by leveraging Artificial Intelligence: A survey. Inform. Med. Unlocked. 2022;29:100832. doi: 10.1016/j.imu.2021.100832. - DOI
-
- Claxton S., Porter P., Brisbane J., Bear N., Wood J., Peltonen V., Della P., Abeyratne U. Identifying acute exacerbations of chronic obstructive pulmonary disease using patient-reported symptoms and cough feature analysis. NPJ Digit. Med. 2021;4:107. doi: 10.1038/s41746-021-00472-x. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

