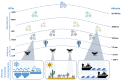
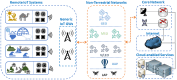
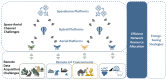
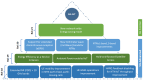
Non-Terrestrial Networks for Energy-Efficient Connectivity of Remote IoT Devices in the 6G Era: A Survey
- PMID: 38400391
- PMCID: PMC10891744
- DOI: 10.3390/s24041227
Non-Terrestrial Networks for Energy-Efficient Connectivity of Remote IoT Devices in the 6G Era: A Survey
Abstract
The Internet of Things (IoT) is gaining popularity and market share, driven by its ability to connect devices and systems that were previously siloed, enabling new applications and services in a cost-efficient manner. Thus, the IoT fuels societal transformation and enables groundbreaking innovations like autonomous transport, robotic assistance, and remote healthcare solutions. However, when considering the Internet of Remote Things (IoRT), which refers to the expansion of IoT in remote and geographically isolated areas where neither terrestrial nor cellular networks are available, internet connectivity becomes a challenging issue. Non-Terrestrial Networks (NTNs) are increasingly gaining popularity as a solution to provide connectivity in remote areas due to the growing integration of satellites and Unmanned Aerial Vehicles (UAVs) with cellular networks. In this survey, we provide the technological framework for NTNs and Remote IoT, followed by a classification of the most recent scientific research on NTN-based IoRT systems. Therefore, we provide a comprehensive overview of the current state of research in IoRT and identify emerging research areas with high potential. In conclusion, we present and discuss 3GPP's roadmap for NTN standardization, which aims to establish an energy-efficient IoRT environment in the 6G era.
Keywords: 5G; 6G; Internet of Remote Things (IoRT); Internet of Things (IoT); non terrestrial networks (NTNs); satellites; unmanned aerial vehicles (UAVs).
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures
References
-
- Bellini P., Nesi P., Pantaleo G. IoT-Enabled Smart Cities: A Review of Concepts, Frameworks and Key Technologies. Appl. Sci. 2022;12:1607. doi: 10.3390/app12031607. - DOI
-
- Vailshery L.S. Number of Internet of Things (IoT) Connected Devices Worldwide from 2019 to 2023, with Forecasts from 2022 to 2030. 2023. [(accessed on 6 February 2024)]. Available online: https://www.statista.com/statistics/1183457/iot-connected-devices-worldw...
-
- Shafique K., Khawaja B.A., Sabir F., Qazi S., Mustaqim M. Internet of Things (IoT) for Next-Generation Smart Systems: A Review of Current Challenges, Future Trends and Prospects for Emerging 5G-IoT Scenarios. IEEE Access. 2020;8:23022–23040. doi: 10.1109/ACCESS.2020.2970118. - DOI
-
- Gupta B., Quamara M. An overview of Internet of Things (IoT): Architectural aspects, challenges, and protocols. Concurr. Comput. Pract. Exp. 2020;32:e4946. doi: 10.1002/cpe.4946. - DOI
-
- Demertzis K., Tsiknas K., Taketzis D., Skoutas D.N., Skianis C., Iliadis L., Zoiros K.E. Communication Network Standards for Smart Grid Infrastructures. Network. 2021;1:132–145. doi: 10.3390/network1020009. - DOI
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials