Sensing Data Concealment in NFTs: A Steganographic Model for Confidential Cross-Border Information Exchange
- PMID: 38400422
- PMCID: PMC10892136
- DOI: 10.3390/s24041264
Sensing Data Concealment in NFTs: A Steganographic Model for Confidential Cross-Border Information Exchange
Abstract
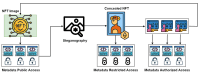
In an era dominated by rapid digitalization of sensed data, the secure exchange of sensitive information poses a critical challenge across various sectors. Established techniques, particularly in emerging technologies like the Internet of Things (IoT), grapple with inherent risks in ensuring data confidentiality, integrity, and vulnerabilities to evolving cyber threats. Blockchain technology, known for its decentralized and tamper-resistant characteristics, stands as a reliable solution for secure data exchange. However, the persistent challenge lies in protecting sensitive information amidst evolving digital landscapes. Among the burgeoning applications of blockchain technology, non-fungible tokens (NFTs) have emerged as digital certificates of ownership, securely recording various types of data on a distributed ledger. Unlike traditional data storage methods, NFTs offer several advantages for secure information exchange. Firstly, their tamperproof nature guarantees the authenticity and integrity of the data. Secondly, NFTs can hold both immutable and mutable data within the same token, simplifying management and access control. Moving beyond their conventional association with art and collectibles, this paper presents a novel approach that utilizes NFTs as dynamic carriers for sensitive information. Our solution leverages the immutable NFT data to serve as a secure data pointer, while the mutable NFT data holds sensitive information protected by steganography. Steganography embeds the data within the NFT, making them invisible to unauthorized eyes, while facilitating portability. This dual approach ensures both data integrity and authorized access, even in the face of evolving digital threats. A performance analysis confirms the approach's effectiveness, demonstrating its reliability, robustness, and resilience against attacks on hidden data. This paves the way for secure data transmission across diverse industries.
Keywords: NFTs; blockchain; steganography.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures




Similar articles
-
Light weight blockchain with IoT devices to secure smart non-fungible tokens using hybrid secure functions.Sci Rep. 2025 Aug 27;15(1):31633. doi: 10.1038/s41598-025-16945-y. Sci Rep. 2025. PMID: 40866409 Free PMC article.
-
Non-fungible tokens (NFTs) in healthcare: a thematic analysis and research agenda.Front Digit Health. 2024 Jun 11;6:1377531. doi: 10.3389/fdgth.2024.1377531. eCollection 2024. Front Digit Health. 2024. PMID: 38919876 Free PMC article.
-
Whole slide images as non-fungible tokens: A decentralized approach to secure, scalable data storage and access.J Pathol Inform. 2023 Nov 9;15:100350. doi: 10.1016/j.jpi.2023.100350. eCollection 2024 Dec. J Pathol Inform. 2023. PMID: 38162951 Free PMC article.
-
Self-sovereign identity empowered non-fungible patient tokenization for health information exchange using blockchain technology.Comput Biol Med. 2023 May;157:106778. doi: 10.1016/j.compbiomed.2023.106778. Epub 2023 Mar 15. Comput Biol Med. 2023. PMID: 36934533
-
A Survey: Security, Transparency, and Scalability Issues of NFT's and Its Marketplaces.Sensors (Basel). 2022 Nov 15;22(22):8833. doi: 10.3390/s22228833. Sensors (Basel). 2022. PMID: 36433429 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Kanagala P. Effective cyber security system to secure optical data based on deep learning approach for healthcare application. Optik. 2023;272:170315. doi: 10.1016/j.ijleo.2022.170315. - DOI
-
- Jin H., Luo Y., Li P., Mathew J. A review of secure and privacy-preserving medical data sharing. IEEE Access. 2019;7:61656–61669. doi: 10.1109/ACCESS.2019.2916503. - DOI
-
- Liu Z., Li Z. A blockchain-based framework of cross-border e-commerce supply chain. Int. J. Inf. Manag. 2020;52:102059. doi: 10.1016/j.ijinfomgt.2019.102059. - DOI
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

