Performance of Subcutaneous Implantable Cardioverter Defibrillator (S-ICD) in Chinese Population with Primary Prevention Indications: A Prospective Observational Cohort Study
- PMID: 38400538
- PMCID: PMC10900845
- DOI: 10.12659/MSM.942747
Performance of Subcutaneous Implantable Cardioverter Defibrillator (S-ICD) in Chinese Population with Primary Prevention Indications: A Prospective Observational Cohort Study
Abstract
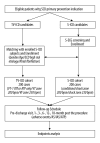
BACKGROUND International studies have shown that use of a subcutaneous implantable cardioverter defibrillator (S-ICD) could reduce lead-related complications while maintaining adequate defibrillation performance; however, data from the Chinese population or other Asian groups are limited. MATERIAL AND METHODS SCOPE is a prospective, multicenter, observational cohort study. Two hundred patients with primary prevention indication for sudden cardiac death (SCD), who are candidates for S-ICD, will be enrolled. From the same population, another 200 patients who are candidates for transvenous implantable cardioverter defibrillator (TV-ICD) will be enrolled after being matched for age, sex, SCD high-risk etiology (ischemic cardiomyopathy, and non-ischemic cardiomyopathy, ion channel disease, and other) and atrial fibrillation in a 1: 1 ratio with enrolled S-ICD patients. All the patients will be followed for 18 months under standard of care. RESULTS The primary endpoint is proportion of patients free from inappropriate shock (IAS) at 18 months in the S-ICD group. The lower 95% confidence bound of the proportion will be compared with a performance goal of 90.3%, which was derived from the previous meta-analysis. The comparisons between S-ICD and TV-ICD on IAS, appropriate shock, and complications will be used as secondary endpoints without formal assumptions. CONCLUSIONS This is the first prospective multicenter study focusing on the long-term performance of S-ICD in a Chinese population. By comparing with the data derived from international historical studies and a matched TV-ICD group, data from SCOPE will allow for the assessment of S-ICD in the Chinese population in a contemporary real-world implantation level and programming techniques, which will help us to further modify the device implantation and programming protocol in this specific population in the future.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures
Similar articles
-
Primary Results From the Understanding Outcomes With the S-ICD in Primary Prevention Patients With Low Ejection Fraction (UNTOUCHED) Trial.Circulation. 2021 Jan 5;143(1):7-17. doi: 10.1161/CIRCULATIONAHA.120.048728. Epub 2020 Oct 19. Circulation. 2021. PMID: 33073614 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial.
-
Postapproval Study of a Subcutaneous Implantable Cardioverter-Defibrillator System.J Am Coll Cardiol. 2023 Aug 1;82(5):383-397. doi: 10.1016/j.jacc.2023.05.034. J Am Coll Cardiol. 2023. PMID: 37495274
-
Subcutaneous versus transvenous implantable cardioverter defibrillators in children and young adults: A meta-analysis.Pacing Clin Electrophysiol. 2022 Dec;45(12):1409-1414. doi: 10.1111/pace.14603. Epub 2022 Oct 27. Pacing Clin Electrophysiol. 2022. PMID: 36214206
-
Subcutaneous versus transvenous implantable defibrillator: An updated meta-analysis.Heart Rhythm. 2021 Mar;18(3):382-391. doi: 10.1016/j.hrthm.2020.11.013. Epub 2020 Nov 16. Heart Rhythm. 2021. PMID: 33212250
-
Subcutaneous Versus Transvenous Implantable Defibrillator Therapy: A Meta-Analysis of Case-Control Studies.JACC Clin Electrophysiol. 2017 Dec 26;3(13):1475-1483. doi: 10.1016/j.jacep.2017.07.017. Epub 2017 Sep 27. JACC Clin Electrophysiol. 2017. PMID: 29759827
References
-
- Zeppenfeld K, Tfelt-Hansen J, de Riva M, et al. 2022 ESC Guidelines for the management of patients with ventricular arrhythmias and the prevention of sudden cardiac death. Eur Heart J. 2022;43(40):3997–4126. - PubMed
-
- Kleemann T, Becker T, Doenges K, et al. Annual rate of transvenous defibrillation lead defects in implantable cardioverter-defibrillators over a period of >10 years. Circulation. 2007;115(19):2474–80. - PubMed
-
- Healey JS, Krahn AD, Bashir J, et al. Perioperative safety and early patient and device outcomes among subcutaneous versus transvenous implantable cardioverter defibrillator implantations: A randomized, multicenter trial. Ann Intern Med. 2022;175(12):1658–65. - PubMed
-
- Knops RE, Olde Nordkamp L, Delnoy P, et al. Subcutaneous or transvenous defibrillator therapy. N Engl J Med. 2020;383(6):526–36. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

