A signature of enhanced proliferation associated with response and survival to anti-PD-L1 therapy in early-stage non-small cell lung cancer
- PMID: 38401548
- PMCID: PMC10982989
- DOI: 10.1016/j.xcrm.2024.101438
A signature of enhanced proliferation associated with response and survival to anti-PD-L1 therapy in early-stage non-small cell lung cancer
Abstract
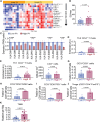
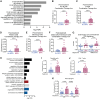
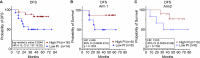
In early-stage non-small cell lung cancer, the combination of neoadjuvant anti-PD-L1 and subablative stereotactic body radiation therapy (SBRT) is associated with higher rates of major pathologic response compared to anti-PD-L1 alone. Here, we identify a 140-gene set, enriched in genes characteristic of highly proliferating cells, associated with response to the dual therapy. Analysis of on-treatment transcriptome data indicate roles for T and B cells in response. The 140-gene set is associated with disease-free survival when applied to the combined trial arms. This 140-gene set identifies a subclass of tumors in all 7 of The Cancer Genome Atlas tumor types examined. Worse survival is associated with the 140-gene signature in 5 of these tumor types. Collectively, our data support that this 140-gene set, discovered in association with response to combined anti-PD-L1 and SBRT, identifies a clinically aggressive subclass of solid tumors that may be more likely to respond to immunotherapies.
Keywords: NSCLC; biomarker immunotherapy response; combination immunotherapy radiation; immunotherapy; radiation therapy; rapidly proliferating tumors.
Copyright © 2024 The Author(s). Published by Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
Conflict of interest statement
Declaration of interests N.K.A. has equity in Angiocrine Bioscience, TMRW, and View Point Medical. O.E. is supported by Janssen, J&J, AstraZeneca, Volastra, and Eli Lilly research grants. He is a scientific advisor and equity holder in Freenome, Owkin, Volastra Therapeutics, and One Three Biotech, and a paid scientific advisor to Champions Oncology. T.E.M. receives research funding from Janssen. Cornell University has filed a patent application on the work described in this paper.
Figures





References
-
- Altorki N.K., McGraw T.E., Borczuk A.C., Saxena A., Port J.L., Stiles B.M., Lee B.E., Sanfilippo N.J., Scheff R.J., Pua B.B., et al. Neoadjuvant durvalumab with or without stereotactic body radiotherapy in patients with early-stage non-small-cell lung cancer: a single-centre, randomised phase 2 trial. Lancet Oncol. 2021;22:824–835. doi: 10.1016/S1470-2045(21)00149-2. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Ban Y., Markowitz G.J., Zou Y., Ramchandani D., Kraynak J., Sheng J., Lee S.B., Wong S.T.C., Altorki N.K., Gao D., Mittal V. Radiation-activated secretory proteins of Scgb1a1 (+) club cells increase the efficacy of immune checkpoint blockade in lung cancer. Nat. Can. (Ott.) 2021;2:919–931. doi: 10.1038/s43018-021-00245-1. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials

