Challenges and strategies associated with CAR-T cell therapy in blood malignancies
- PMID: 38402232
- PMCID: PMC10893672
- DOI: 10.1186/s40164-024-00490-x
Challenges and strategies associated with CAR-T cell therapy in blood malignancies
Abstract
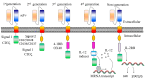
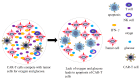
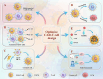
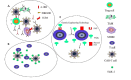
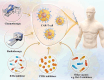
Cellular immunotherapy, particularly CAR-T cells, has shown potential in the improvement of outcomes in patients with refractory and recurrent malignancies of the blood. However, achieving sustainable long-term complete remission for blood cancer remains a challenge, with resistance and relapse being expected outcomes for many patients. Although many studies have attempted to clarify the mechanisms of CAR-T cell therapy failure, the mechanism remains unclear. In this article, we discuss and describe the current state of knowledge regarding these factors, which include elements that influence the CAR-T cell, cancer cells as a whole, and the microenvironment surrounding the tumor. In addition, we propose prospective approaches to overcome these obstacles in an effort to decrease recurrence rates and extend patient survival subsequent to CAR-T cell therapy.
Keywords: CAR-T cell therapy; Hematologic malignancies; Resistance and relapse mechanisms.
© 2024. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Relapse after CAR-T cell therapy in B-cell malignancies: challenges and future approaches.J Zhejiang Univ Sci B. 2022 Oct 15;23(10):793-811. doi: 10.1631/jzus.B2200256. J Zhejiang Univ Sci B. 2022. PMID: 36226535 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Clinical determinants of relapse following CAR-T therapy for hematologic malignancies: Coupling active strategies to overcome therapeutic limitations.Curr Res Transl Med. 2022 Jan;70(1):103320. doi: 10.1016/j.retram.2021.103320. Epub 2021 Nov 9. Curr Res Transl Med. 2022. PMID: 34768218 Review.
-
Resistance and recurrence of malignancies after CAR-T cell therapy.Exp Cell Res. 2022 Jan 15;410(2):112971. doi: 10.1016/j.yexcr.2021.112971. Epub 2021 Dec 11. Exp Cell Res. 2022. PMID: 34906583 Review.
-
Relapse Mechanism and Treatment Strategy After Chimeric Antigen Receptor T-Cell Therapy in Treating B-Cell Hematological Malignancies.Technol Cancer Res Treat. 2022 Jan-Dec;21:15330338221118413. doi: 10.1177/15330338221118413. Technol Cancer Res Treat. 2022. PMID: 35989682 Free PMC article.
-
CAR-T cell therapy for hematological malignancies: Limitations and optimization strategies.Front Immunol. 2022 Sep 28;13:1019115. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2022.1019115. eCollection 2022. Front Immunol. 2022. PMID: 36248810 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Anti-IL-1RAP scFv-mSA-S19-TAT fusion carrier as a multifunctional platform for versatile delivery of biotinylated payloads to myeloid leukemia cells.Sci Rep. 2024 Oct 23;14(1):25080. doi: 10.1038/s41598-024-76851-7. Sci Rep. 2024. PMID: 39443595 Free PMC article.
-
Advancing CAR-based cell therapies for solid tumours: challenges, therapeutic strategies, and perspectives.Mol Cancer. 2025 Jul 7;24(1):191. doi: 10.1186/s12943-025-02386-8. Mol Cancer. 2025. PMID: 40624498 Free PMC article. Review.
-
BCMA-targeted therapies in multiple myeloma: advances, challenges and future prospects.Med Oncol. 2025 May 8;42(6):204. doi: 10.1007/s12032-025-02753-x. Med Oncol. 2025. PMID: 40338452 Review.
-
BRD4 inhibitor reduces exhaustion and blocks terminal differentiation in CAR-T cells by modulating BATF and EGR1.Biomark Res. 2024 Oct 15;12(1):124. doi: 10.1186/s40364-024-00667-w. Biomark Res. 2024. PMID: 39407311 Free PMC article.
-
A Comprehensive Review About the Use of Monoclonal Antibodies in Cancer Therapy.Antibodies (Basel). 2025 Apr 11;14(2):35. doi: 10.3390/antib14020035. Antibodies (Basel). 2025. PMID: 40265416 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Martin T, Usmani SZ, Berdeja JG, Agha M, Cohen AD, Hari P, Avigan D, Deol A, Htut M, Lesokhin A, et al. Ciltacabtagene Autoleucel, an Anti-B-cell Maturation Antigen Chimeric Antigen Receptor T-Cell Therapy, for Relapsed/Refractory multiple myeloma: CARTITUDE-1 2-Year Follow-Up. J Clin Oncology: Official J Am Soc Clin Oncol. 2023;41(6):1265–74. - PMC - PubMed
-
- Munshi NC, Anderson LD, Jr, Shah N, Madduri D, Berdeja J, Lonial S, Raje N, Lin Y, Siegel D, Oriol A, et al. Idecabtagene Vicleucel in Relapsed and Refractory multiple myeloma. N Engl J Med. 2021;384(8):705–16. - PubMed
-
- Abramson JS, Palomba ML, Gordon LI, Lunning MA, Wang M, Arnason J, Mehta A, Purev E, Maloney DG, Andreadis C, et al. Lisocabtagene maraleucel for patients with relapsed or refractory large B-cell lymphomas (TRANSCEND NHL 001): a multicentre seamless design study. Lancet (London England) 2020;396(10254):839–52. - PubMed
-
- Iacoboni G, Rejeski K, Villacampa G, van Doesum JA, Chiappella A, Bonifazi F, Lopez-Corral L, van Aalderen M, Kwon M, Martínez-Cibrian N, et al. Real-world evidence of brexucabtagene autoleucel for the treatment of relapsed or refractory mantle cell lymphoma. Blood Adv. 2022;6(12):3606–10. - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

