Single-molecule RNA sizing enables quantitative analysis of alternative transcription termination
- PMID: 38402271
- PMCID: PMC10894232
- DOI: 10.1038/s41467-024-45968-8
Single-molecule RNA sizing enables quantitative analysis of alternative transcription termination
Abstract
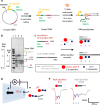
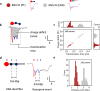
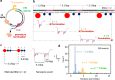
Transcription, a critical process in molecular biology, has found many applications in RNA synthesis, including mRNA vaccines and RNA therapeutics. However, current RNA characterization technologies suffer from amplification and enzymatic biases that lead to loss of native information. Here, we introduce a strategy to quantitatively study both transcription and RNA polymerase behaviour by sizing RNA with RNA nanotechnology and nanopores. To begin, we utilize T7 RNA polymerase to transcribe linear DNA lacking termination sequences. Surprisingly, we discover alternative transcription termination in the origin of replication sequence. Next, we employ circular DNA without transcription terminators to perform rolling circle transcription. This allows us to gain valuable insights into the processivity and transcription behaviour of RNA polymerase at the single-molecule level. Our work demonstrates how RNA nanotechnology and nanopores may be used in tandem for the direct and quantitative analysis of RNA transcripts. This methodology provides a promising pathway for accurate RNA structural mapping by enabling the study of full-length RNA transcripts at the single-molecule level.
© 2024. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
F.B. and U.F.K. are inventors of two patents related to RNA analysis with nanopores (UK patent application no. 2113935.7, in process; UK Patent application nos. 2112088.6 and PCT/GB2022/052171, in process) submitted by Cambridge Enterprise on behalf of the University of Cambridge. U.F.K. is a co-founder of Cambridge Nucleomics. The remaining authors declare no competing interests.
Figures

References
-
- Sousa, R. & Mukherjee, S. T7 RNA Polymerase. Prog. Nucleic Acid Res. Mol. Biol.73, 1–41 (2003). - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

