Prognostic significance of IL-18 in acute coronary syndrome patients
- PMID: 38402570
- PMCID: PMC10823553
- DOI: 10.1002/clc.24229
Prognostic significance of IL-18 in acute coronary syndrome patients
Abstract
Background: After acute coronary syndrome (ACS), inflammation aids healing but may harm the heart. Interleukin (IL)-18 and IL-1β are pivotal proinflammatory cytokines released during pyroptosis, a process that initiates and sustains inflammation. This study aimed to evaluate the levels of circulating IL-18 and IL-1β during the progression of ACS and to determine their association with subsequent clinical events in ACS patients.
Hypothesis: Circulating levels of IL-18 and IL-1β are associated with subsequent clinical events in ACS patients.
Methods: Employing immunoassays, we examined plasma levels of IL-1β and IL-18 in 159 ACS patients and matched them with 159 healthy controls. The primary composite endpoint included recurrent unstable angina, myocardial infarction, heart failure exacerbation, stroke, or cardiovascular death.
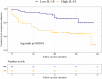
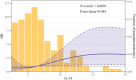
Results: ACS patients exhibited a significant increase in plasma IL-18 levels, measuring 6.36 [4.46-9.88] × 102 pg/mL, in contrast to the control group with levels at 4.04 [3.21-4.94] × 102 pg/mL (p < 0.001). Conversely, plasma levels of IL-1β remained unchanged compared to the control group. Following a 25-month follow-up, IL-18 levels exceeding the median remained an important prognostic factor for adverse clinical events in ACS patients (hazard ratio = 2.37, 95% confidence interval: 1.14-4.91, p = 0.021). Besides, IL-18 displayed a nonlinear association with adverse clinical events (p nonlinear = 0.044). Subgroup analysis revealed that the correlation between IL-18 and the risk of adverse clinical events was not significantly affected by factors such as age, sex, history of diabetes, smoking, Gensini score, or ACS type (all p interaction >0.05).
Conclusion: IL-18 appears to hold potential as a predictive marker for anticipating clinical outcomes in patients with ACS.
Keywords: acute coronary syndrome; adverse clinical events; inflammation; interleukin-18; interleukin-1β; prognosis.
© 2024 The Authors. Clinical Cardiology published by Wiley Periodicals, LLC.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Interleukin-6 and the Risk of Adverse Outcomes in Patients After an Acute Coronary Syndrome: Observations From the SOLID-TIMI 52 (Stabilization of Plaque Using Darapladib-Thrombolysis in Myocardial Infarction 52) Trial.J Am Heart Assoc. 2017 Oct 24;6(10):e005637. doi: 10.1161/JAHA.117.005637. J Am Heart Assoc. 2017. PMID: 29066436 Free PMC article.
-
Interleukin-18/interleukin-10 ratio is an independent predictor of recurrent coronary events during a 1-year follow-up in patients with acute coronary syndrome.Int J Cardiol. 2007 May 2;117(3):333-9. doi: 10.1016/j.ijcard.2006.05.017. Epub 2006 Jul 20. Int J Cardiol. 2007. PMID: 16859776
-
Interleukin-18: an independent predictor of cardiovascular events in patients with acute coronary syndrome after 6 months of follow-up.Coron Artery Dis. 2009 Aug;20(5):327-331. doi: 10.1097/mca.0b013e32832e5c73. Coron Artery Dis. 2009. PMID: 19593889
-
Prognostic Role of Elevated Myeloperoxidase in Patients with Acute Coronary Syndrome: A Systemic Review and Meta-Analysis.Mediators Inflamm. 2019 Jun 25;2019:2872607. doi: 10.1155/2019/2872607. eCollection 2019. Mediators Inflamm. 2019. PMID: 31341419 Free PMC article.
-
Novel oral anticoagulants in acute coronary syndrome.Int J Cardiol. 2013 Sep 10;167(6):2449-55. doi: 10.1016/j.ijcard.2012.08.014. Epub 2012 Sep 16. Int J Cardiol. 2013. PMID: 22989603 Review.
Cited by
-
Metabolic Syndrome and Psoriasis: Pivotal Roles of Chronic Inflammation and Gut Microbiota.Int J Mol Sci. 2024 Jul 25;25(15):8098. doi: 10.3390/ijms25158098. Int J Mol Sci. 2024. PMID: 39125666 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Cytokine Gene Variants as Predisposing Factors for the Development and Progression of Coronary Artery Disease: A Systematic Review.Biomolecules. 2024 Dec 19;14(12):1631. doi: 10.3390/biom14121631. Biomolecules. 2024. PMID: 39766338 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Ridker PM, Bhatt DL, Pradhan AD, Glynn RJ, MacFadyen JG, Nissen SE. Inflammation and cholesterol as predictors of cardiovascular events among patients receiving statin therapy: a collaborative analysis of three randomised trials. Lancet. 2023;401(10384):1293‐1301. 10.1016/S0140-6736(23)00215-5 - DOI - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

