Allosteric inhibition of tRNA synthetase Gln4 by N-pyrimidinyl-β-thiophenylacrylamides exerts highly selective antifungal activity
- PMID: 38402621
- PMCID: PMC11031294
- DOI: 10.1016/j.chembiol.2024.01.010
Allosteric inhibition of tRNA synthetase Gln4 by N-pyrimidinyl-β-thiophenylacrylamides exerts highly selective antifungal activity
Abstract
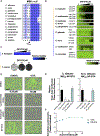
Candida species are among the most prevalent causes of systemic fungal infections, which account for ∼1.5 million annual fatalities. Here, we build on a compound screen that identified the molecule N-pyrimidinyl-β-thiophenylacrylamide (NP-BTA), which strongly inhibits Candida albicans growth. NP-BTA was hypothesized to target C. albicans glutaminyl-tRNA synthetase, Gln4. Here, we confirmed through in vitro amino-acylation assays NP-BTA is a potent inhibitor of Gln4, and we defined how NP-BTA arrests Gln4's transferase activity using co-crystallography. This analysis also uncovered Met496 as a critical residue for the compound's species-selective target engagement and potency. Structure-activity relationship (SAR) studies demonstrated the NP-BTA scaffold is subject to oxidative and non-oxidative metabolism, making it unsuitable for systemic administration. In a mouse dermatomycosis model, however, topical application of the compound provided significant therapeutic benefit. This work expands the repertoire of antifungal protein synthesis target mechanisms and provides a path to develop Gln4 inhibitors.
Keywords: Candida; Gln4; antifungal; fungal pathogens; glutaminyl-tRNA synthetase; translation inhibitor.
Copyright © 2024 The Author(s). Published by Elsevier Ltd.. All rights reserved.
Conflict of interest statement
Declaration of interests L.E.C. and L.W. are co-founders and shareholders in Bright Angel Therapeutics, a platform company for development of novel antifungal therapeutics. L.E.C. is a science advisor for Kapoose Creek, a company that harnesses the therapeutic potential of fungi.
Figures


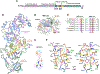



References
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

