Insights into the roles of inositol hexakisphosphate kinase 1 (IP6K1) in mammalian cellular processes
- PMID: 38403246
- PMCID: PMC11065760
- DOI: 10.1016/j.jbc.2024.107116
Insights into the roles of inositol hexakisphosphate kinase 1 (IP6K1) in mammalian cellular processes
Abstract
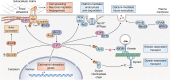
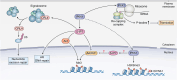
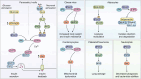
Inositol phosphates and their metabolites play a significant role in several biochemical pathways, gene expression regulation, and phosphate homeostasis. Among the different inositol phosphates, inositol hexakisphosphate (IP6) is a substrate of inositol hexakisphosphate kinases (IP6Ks), which phosphorylate one or more of the IP6 phosphate groups. Pyrophosphorylation of IP6 leads to the formation of inositol pyrophosphates, high-energy signaling molecules that mediate physiological processes through their ability to modify target protein activities, either by directly binding to their target protein or by pyrophosphorylating protein serine residues. 5-diphosphoinositol pentakisphosphate, the most abundant inositol pyrophosphate in mammals, has been extensively studied and found to be significantly involved in a wide range of physiological processes. Three IP6K (IP6K1, IP6K2, and IP6K3) isoforms regulate IP7 synthesis in mammals. Here, we summarize our current understanding of IP6K1's roles in cytoskeletal remodeling, trafficking, cellular migration, metabolism, gene expression, DNA repair, and immunity. We also briefly discuss current gaps in knowledge, highlighting the need for further investigation.
Keywords: 5-IP7; cell migration; gene expression; inositol phosphate; inositol pyrophosphates; metabolism; phosphorylation.
Copyright © 2024 The Authors. Published by Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
Conflict of interest statement
Conflict of interest The authors declare that they have no conflicts of interest with the contents of this article.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Inositol Pyrophosphates: Signaling Molecules with Pleiotropic Actions in Mammals.Molecules. 2020 May 8;25(9):2208. doi: 10.3390/molecules25092208. Molecules. 2020. PMID: 32397291 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Deletion of inositol hexakisphosphate kinase 1 (IP6K1) reduces cell migration and invasion, conferring protection from aerodigestive tract carcinoma in mice.Cell Signal. 2016 Aug;28(8):1124-36. doi: 10.1016/j.cellsig.2016.04.011. Epub 2016 Apr 30. Cell Signal. 2016. PMID: 27140681 Free PMC article.
-
Inositol Pyrophosphates as Versatile Metabolic Messengers.Annu Rev Biochem. 2024 Aug;93(1):317-338. doi: 10.1146/annurev-biochem-030222-121901. Annu Rev Biochem. 2024. PMID: 39094034 Review.
-
Inositol hexakisphosphate kinase 1 (IP6K1) activity is required for cytoplasmic dynein-driven transport.Biochem J. 2016 Oct 1;473(19):3031-47. doi: 10.1042/BCJ20160610. Epub 2016 Jul 29. Biochem J. 2016. PMID: 27474409 Free PMC article.
-
The inositol hexakisphosphate kinases IP6K1 and -2 regulate human cellular phosphate homeostasis, including XPR1-mediated phosphate export.J Biol Chem. 2019 Jul 26;294(30):11597-11608. doi: 10.1074/jbc.RA119.007848. Epub 2019 Jun 11. J Biol Chem. 2019. PMID: 31186349 Free PMC article.
Cited by
-
On the Possible Effect of Phytic Acid (Myo-Inositol Hexaphosphoric Acid, IP6) on Cytochromes P450 and Systems of Xenobiotic Metabolism in Different Hepatic Models.Int J Mol Sci. 2024 Mar 23;25(7):3610. doi: 10.3390/ijms25073610. Int J Mol Sci. 2024. PMID: 38612422 Free PMC article.
-
Valproate independently activates Snf1, inhibits TORC1, and induces repression of INO1 transcription by increasing nuclear localization of Opi1.Sci Rep. 2025 Jul 9;15(1):24601. doi: 10.1038/s41598-025-07540-2. Sci Rep. 2025. PMID: 40634329 Free PMC article.
-
Inositol Phosphates and Synthesizing Enzymes: Implications in Neurodegenerative Disorders.Biomolecules. 2025 Feb 4;15(2):225. doi: 10.3390/biom15020225. Biomolecules. 2025. PMID: 40001529 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Inositols and Bone Health: Potential Therapeutic Applications in Osteoporosis Prevention and Treatment.Nutrients. 2025 Jun 13;17(12):1999. doi: 10.3390/nu17121999. Nutrients. 2025. PMID: 40573111 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Towards Improved Bioavailability of Cereal Inositol Phosphates, Myo-Inositol and Phenolic Acids.Molecules. 2025 Feb 1;30(3):652. doi: 10.3390/molecules30030652. Molecules. 2025. PMID: 39942756 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Michigami T., Kawai M., Yamazaki M., Ozono K. Phosphate as a signaling molecule and its sensing mechanism. Physiol. Rev. 2018;98:2317–2348. - PubMed
-
- Saiardi A., Erdjument-Bromage H., Snowman A.M., Tempst P., Snyder S.H. Synthesis of diphosphoinositol pentakisphosphate by a newly identified family of higher inositol polyphosphate kinases. Curr. Biol. 1999;9:1323–1326. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

