Role of chemokines in regulating luteal and uterine functions in pregnant cows
- PMID: 38403584
- PMCID: PMC11153120
- DOI: 10.1262/jrd.2023-100
Role of chemokines in regulating luteal and uterine functions in pregnant cows
Abstract
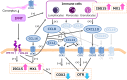
Pregnancy is intricately regulated by the interactions between various bioactive substances secreted by the conceptus, uterus, and corpus luteum (CL). Interferon-τ, synthesized and secreted by the conceptus, plays a central role in the interaction mechanism of maternal recognition in cows. Chemokines, chemotaxis mediators that are primarily secreted by immune cells, regulate various reproductive responses in various species. Although there are scattered reports on the potential roles of chemokines in the bovine CL and the uterus during the estrous cycle, there is little information on chemokines in these organs during pregnancy. Therefore, in this review, we discuss the possible physiological roles of chemokines in the CL and uterus of pregnant cows, focusing on our recent findings on chemokines and changes in their receptor expression in the CL and endometrium of cows at some stages of pregnancy.
Keywords: Chemokines; Corpus luteum; Cow; Pregnancy; Uterus.
Figures
References
-
- Thatcher WW, Bartol FF, Knickerbocker JJ, Curl JS, Wolfenson D, Bazer FW, Roberts RM. Maternal recognition of pregnancy in cattle. J Dairy Sci 1984; 67: 2797–2811. - PubMed
-
- Bazer FW. Mediators of maternal recognition of pregnancy in mammals. Proc Soc Exp Biol Med 1992; 199: 373–384. - PubMed
-
- Lafrance M, Goff AK. Effect of pregnancy on oxytocin-induced release of prostaglandin F2 α in heifers. Biol Reprod 1985; 33: 1113–1119. - PubMed
-
- Binelli M, Guzeloglu A, Badinga L, Arnold DR, Sirois J, Hansen TR, Thatcher WW. Interferon-τ modulates phorbol ester-induced production of prostaglandin and expression of cyclooxygenase-2 and phospholipase-A(2) from bovine endometrial cells. Biol Reprod 2000; 63: 417–424. - PubMed
-
- Niswender GD, Juengel JL, Silva PJ, Rollyson MK, McIntush EW. Mechanisms controlling the function and life span of the corpus luteum. Physiol Rev 2000; 80: 1–29. - PubMed

