The effect of Astragali Radix-Radix Angelica Sinensis on acute kidney injury: a network pharmacology and molecular docking study
- PMID: 38404557
- PMCID: PMC10891378
- DOI: 10.21037/tau-23-562
The effect of Astragali Radix-Radix Angelica Sinensis on acute kidney injury: a network pharmacology and molecular docking study
Abstract
Background: Acute kidney injury (AKI) is a devastating clinical syndrome with high mortality rate attributed to lack of effective treatment. The herbal pair of Astragali Radix (AR) and Radix Angelica Sinensis (RAS) is a commonly prescribed herbal formula or is added to other traditional Chinese medicine (TCM) prescriptions for the treatment of kidney diseases. AR-RAS has certain protective effects on AKI in experiments, but the relevant mechanisms have yet to be clear. So this study aims to explore the mechanism of action of AR-RAS in AKI by combining network pharmacology and molecular docking methods.
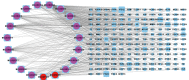
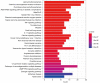
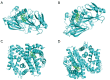
Methods: In Traditional Chinese Medicine Systems Pharmacology Database and Analysis Platform (TCMSP), the major AR-RAS chemical components and associated action targets were found and screened. The DrugBank and GeneCards databases were used to find AKI-related targets. The targets that are in close relationship with AKI were obtained from Therapeutic Target database (TTD), Online Mendelian Inheritance in Man (OMIM), and PharmGKB databases. The "herb-active ingredient-target" network was drawn by Cytoscape 3.8.0 software. The Search Tool for the Retrieval of Interacting Genes/Proteins (STRING) database was used to build the protein-protein interaction network. Bioconductor/R was used to examine Gene Ontology (GO) function and Kyoto Encyclopedia of Genes and Genomes (KEGG) pathway enrichment. AR-RAS components and critical targets were docked using the AutoDock Vina program.
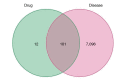
Results: A compound-target network, built by screening and analyzing the results, allowed to identify 19 active components and 101 possible therapeutic targets for AKI. The main ingredients were quercetin, kaempferol, 7-o-methylisocronulatol, formononetin and isorhamnetin. The key targets included AKT serine/threonine kinase 1 (AKT1), nuclear receptor coactivator 1 (NCOA1), JUN, estrogen receptor alpha (ESR1) and mitogen-activated protein kinase 8 (MAPK8). These molecules are targeted by pathways such as the calcium signaling route, the tumor necrosis factor (TNF) signaling pathway and the interleukin-17 (IL-17) signaling pathway, as well as the development of T helper 17 cells. Molecular docking demonstrated that AR-active RAS components exhibited strong binding activities to probable targets of AKI.
Conclusions: We described here the potential active ingredients, possible targets responsible for the efficacy of AR-RAS in AKI treatment, providing a theoretical basis for further research.
Keywords: Astragali Radix-Radix Angelica Sinensis (AR-RAS); acute kidney injury (AKI); molecular docking; network pharmacology.
2024 Translational Andrology and Urology. All rights reserved.
Conflict of interest statement
Conflicts of Interest: All authors have completed the ICMJE uniform disclosure form (available at https://tau.amegroups.com/article/view/10.21037/tau-23-562/coif). The authors have no conflicts of interest to declare.
Figures



Similar articles
-
The potential mechanism of Astragali Radix in the treatment of children with nephrotic syndrome.Transl Pediatr. 2021 Sep;10(9):2298-2306. doi: 10.21037/tp-21-348. Transl Pediatr. 2021. PMID: 34733670 Free PMC article.
-
Network Pharmacology and Molecular Docking-Based Investigation of Potential Targets of Astragalus membranaceus and Angelica sinensis Compound Acting on Spinal Cord Injury.Dis Markers. 2022 Sep 15;2022:2141882. doi: 10.1155/2022/2141882. eCollection 2022. Dis Markers. 2022. Retraction in: Dis Markers. 2023 Jul 26;2023:9824032. doi: 10.1155/2023/9824032. PMID: 36157206 Free PMC article. Retracted.
-
[Anti-rheumatoid arthritis mechanism of Sophorae Tonkinesis Radix et Rhizoma based on network pharmacology and experimental verification].Zhongguo Zhong Yao Za Zhi. 2022 Oct;47(19):5327-5335. doi: 10.19540/j.cnki.cjcmm.20220526.401. Zhongguo Zhong Yao Za Zhi. 2022. PMID: 36472040 Chinese.
-
Network pharmacology and molecular docking technology for exploring the effect and mechanism of Radix Bupleuri and Radix Paeoniae Alba herb-pair on anti-hepatitis: A review.Medicine (Baltimore). 2023 Dec 1;102(48):e35443. doi: 10.1097/MD.0000000000035443. Medicine (Baltimore). 2023. PMID: 38050220 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Exploration of the mechanism of Zisheng Shenqi decoction against gout arthritis using network pharmacology.Comput Biol Chem. 2021 Feb;90:107358. doi: 10.1016/j.compbiolchem.2020.107358. Epub 2020 Aug 8. Comput Biol Chem. 2021. PMID: 33243703 Review.
Cited by
-
Shensu IV maintains the integrity of the glomerular filtration barrier and exerts renal protective effects by regulating endogenous hydrogen sulfide levels.Front Pharmacol. 2024 Dec 9;15:1447249. doi: 10.3389/fphar.2024.1447249. eCollection 2024. Front Pharmacol. 2024. PMID: 39720588 Free PMC article.
References
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous
