Acute effects of sodium citrate supplementation on competitive performance and lactate level of elite fitness challenge athletes: A crossover, placebo-controlled, double-blind study
- PMID: 38404749
- PMCID: PMC10885582
- DOI: 10.1016/j.jesf.2024.02.001
Acute effects of sodium citrate supplementation on competitive performance and lactate level of elite fitness challenge athletes: A crossover, placebo-controlled, double-blind study
Abstract
Purpose: The performance of sodium citrate has been investigated in high-intensity exercises, but fewer studies have addressed the role of citrate in weight-bearing exercises.
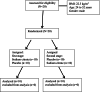
Methods: Twenty fitness challenge athletes, aged 24-32 years, volunteered to participate in this crossover, placebo-controlled, double-blind study. Initially, ten athletes were given a placebo and asked to complete a fitness challenge (i.e., chin-ups, squat jumps, dips, walking lunges, sit-ups, and burpees-devil press). Another ten athletes were supplemented with sodium citrate 0.5 g/kg body mass supplements 3 h prior to performing the fitness challenges. The same procedures were completed two days later with the supplement and placebo dextrose groups switched in a cross-over design. Athletes and assessors were blinded for the experimental condition (placebo vs. verum). Lactate levels were measured 5 min after exercise. The athletes' performance on each item of the fitness challenge as well as their lactate levels, were compared. Differences between the means of the measured variables were contrasted using a dependent t-test.
Results: Supplementing sodium citrate substantially improved athletes' performance in all six fitness challenge items (p < 0.05, 0.69<Cohen's d < 2.52, moderate to large). In addition, lactate levels registered after the fitness challenge were lower in the citrate sodium supplementation vs. placebo condition (p = 0.001, Cohen's d = 0.63, moderate).
Conclusion: Acute sodium citrate supplementation may help fitness challengers postpone muscular fatigue and increase performance, potentially via the prevention of lactate accumulation.
Keywords: Anaerobic performance; Dietary supplement; Lactatemia; Sodium citrate.
© 2024 The Society of Chinese Scholars on Exercise Physiology and Fitness. Published by Elsevier (Singapore) Pte Ltd.
Conflict of interest statement
A conflict of interest occurs when an individual's objectivity is potentially compromised by a desire for financial gain, prominence, professional advancement or a successful outcome. JESF Editors strive to ensure that what is published in the Journal is as balanced, objective and evidence-based as possible. Since it can be difficult to distinguish between an actual conflict of interest and a perceived conflict of interest, the Journal requires authors to disclose all and any potential conflicts of interest.
Similar articles
-
Influence of caffeine and sodium citrate ingestion on 1,500-m exercise performance in elite wheelchair athletes: a pilot study.Int J Sport Nutr Exerc Metab. 2014 Jun;24(3):296-304. doi: 10.1123/ijsnem.2013-0127. Epub 2013 Nov 25. Int J Sport Nutr Exerc Metab. 2014. PMID: 24281893 Clinical Trial.
-
Chronic Ingestion of Sodium and Potassium Bicarbonate, with Potassium, Magnesium and Calcium Citrate Improves Anaerobic Performance in Elite Soccer Players.Nutrients. 2018 Nov 1;10(11):1610. doi: 10.3390/nu10111610. Nutrients. 2018. PMID: 30388775 Free PMC article.
-
The Effects of Sodium Citrate Ingestion on Metabolism and 1500-m Racing Time in Trained Female Runners.J Sports Sci Med. 2008 Mar 1;7(1):125-31. eCollection 2008. J Sports Sci Med. 2008. PMID: 24150144 Free PMC article.
-
The Effects of Resistance Training on Muscular Fitness, Muscle Morphology, and Body Composition in Elite Female Athletes: A Systematic Review.Sports Med. 2023 Sep;53(9):1709-1735. doi: 10.1007/s40279-023-01859-4. Epub 2023 Jun 8. Sports Med. 2023. PMID: 37289331 Free PMC article.
-
Effects of acute alkalosis and acidosis on performance: a meta-analysis.Sports Med. 2011 Oct 1;41(10):801-14. doi: 10.2165/11591440-000000000-00000. Sports Med. 2011. PMID: 21923200 Review.
References
-
- Amirsasan R., Nabilpour M., Pourraze H., Curby D. Effect of 8-week resistance training with creatine supplementation on body composition and physical fitness indexes in male futsal players. Int J Sport Stud Hlth. 2018;1
-
- Paryab N., Taheri M., H'Mida C., et al. Melatonin supplementation improves psychomotor and physical performance in collegiate student-athletes following a sleep deprivation night. Chronobiol Int. 2021;38:753–761. - PubMed
-
- Motavari M., Seifi-Skishahr F., Nabilpour M., Mayhew J., Mamshali E., Afroundeh R. The effect of vitamin D supplementation after resistance training on physiological characteristics in futsal players with vitamin D deficiency. Int J Sport Stud Health. 2022;5
-
- Jahani M., Nabilpour M., Campillo R.R. Effects of L-arginine supplementation and aerobic training on hemodynamic indices of obese men. Int J Sport Stud Health. 2019;2
-
- Girard O., Millet G.P. Neuromuscular fatigue in racquet sports. Phys Med Rehabil Clin. 2009;20:161–173. ix. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources