To explore the potential mechanisms of cognitive impairment in children with MRI-negative pharmacoresistant epilepsy due to focal cortical dysplasia: A pilot study from gray matter structure view
- PMID: 38404806
- PMCID: PMC10884915
- DOI: 10.1016/j.heliyon.2024.e26609
To explore the potential mechanisms of cognitive impairment in children with MRI-negative pharmacoresistant epilepsy due to focal cortical dysplasia: A pilot study from gray matter structure view
Abstract
Objectives: To investigate the characteristics of brain structure in children with focal cortical dysplasia (FCD)-induced pharmacoresistant epilepsy, and explore the potential mechanisms of cognitive impairment from the view of gray matter alteration.
Methods: 25 pharmacoresistant pediatric patients with pathologically confirmed focal cortical dysplasia (FCD), and 25 gender-matched healthy controls were included in this study. 3.0T MRI data and intelligence tests using the Wechsler Intelligence Scale for Children-Forth Edition (WISC-IV) were generated for all subjects. Voxel-based morphometry (VBM)-diffeomorphic anatomical registration through exponentiated lie algebra (DARTEL) and surface-based morphometry (SBM) analyses were performed to analyze gray matter volume and cortical structure. Two-sample t-tests were used to compare the differences in gray matter volume (P<0.05, FWE) and cortical thickness (P<0.001, FWE) between the two groups. Also, the Spearman rank correlation analyses were employed to determine the relationship between structural alterations and neuropsychological results.
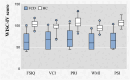
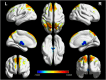
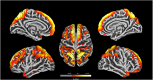
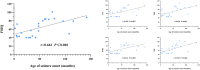
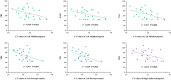
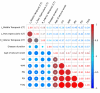
Results: The WISC-IV scores of the FCD group were significantly lower than those of the HC group in terms of full-scale intelligence quotient (FSIQ), verbal comprehension index (VCI), perceptual reasoning index (PRI), working memory index (WMI), and processing speed index (PSI) (all P<0.01). Compared with the HC group, in the FCD group, the gray matter volume (GMV) reduced significantly in the left cerebellum_8, cerebellum_Crus2, and bilateral thalamus (P<0.05, FWE); the GMV increased in the bilateral medial frontal gyrus, right precuneus, and left inferior temporal gyrus (P<0.05, FWE), and the cortical thickness increased in the bilateral frontal, parietal, and temporal areas (P<0.001, FWE). Correlation analyses showed that the age of seizure onset had positive correlations with the WISC-IV scores significantly. Meanwhile, the cortex thicknesses of the left pars opercularis gyrus, left middle temporal gyrus, and right inferior temporal gyrus had negative correlations with the WISC-IV scores significantly.
Conclusion: FCD patients showed subtle structural abnormalities in multiple brain regions, with significant involvement of the primary visual cortex and language function cortex. And we also demonstrated a crucial correlation between gray matter structural alteration and cognitive impairment.
Keywords: Cognitive function; Focal cortical dysplasia; Magnetic resonance imaging; Pharmacoresistant epilepsy; Structural abnormalities.
© 2024 The Authors. Published by Elsevier Ltd.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Cognitive impairment and gray/white matter volume abnormalities in pediatric patients with Turner syndrome presenting with various karyotypes.J Pediatr Endocrinol Metab. 2013;26(11-12):1111-21. doi: 10.1515/jpem-2013-0145. J Pediatr Endocrinol Metab. 2013. PMID: 23846137
-
Correlations Between Structural Brain Abnormalities, Cognition and Electroclinical Characteristics in Patients With Juvenile Myoclonic Epilepsy.Front Neurol. 2022 May 16;13:883078. doi: 10.3389/fneur.2022.883078. eCollection 2022. Front Neurol. 2022. PMID: 35651335 Free PMC article.
-
Cortical and subcortical morphometric changes in patients with frontal focal cortical dysplasia type II.Neuroradiology. 2025 Mar;67(3):657-664. doi: 10.1007/s00234-024-03471-3. Epub 2024 Sep 21. Neuroradiology. 2025. PMID: 39305355
-
Gray Matter Structural Alterations in Social Anxiety Disorder: A Voxel-Based Meta-Analysis.Front Psychiatry. 2018 Sep 21;9:449. doi: 10.3389/fpsyt.2018.00449. eCollection 2018. Front Psychiatry. 2018. PMID: 30298028 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Cortical and Subcortical Gray Matter Volume in Youths With Conduct Problems: A Meta-analysis.JAMA Psychiatry. 2016 Jan;73(1):64-72. doi: 10.1001/jamapsychiatry.2015.2423. JAMA Psychiatry. 2016. PMID: 26650724 Review.
References
-
- Lamberink H.J., Otte W.M., Blümcke I., Braun K. Seizure outcome and use of antiepileptic drugs after epilepsy surgery according to histopathological diagnosis: a retrospective multicentre cohort study. Lancet. Neurol. 2020;19(9):748–757. - PubMed
-
- Fauser S., Huppertz H.J., Bast T., Strobl K., Pantazis G., Altenmueller D.M., et al. Clinical characteristics in focal cortical dysplasia: a retrospective evaluation in a series of 120 patients. Brain. 2006;129(Pt 7):1907–1916. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

