Unilateral external fixator and its biomechanical effects in treating different types of femoral fracture: A finite element study with experimental validated model
- PMID: 38404809
- PMCID: PMC10884926
- DOI: 10.1016/j.heliyon.2024.e26660
Unilateral external fixator and its biomechanical effects in treating different types of femoral fracture: A finite element study with experimental validated model
Abstract
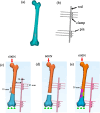
Previous works had successfully demonstrated the clinical effectiveness of unilateral external fixator in treating various types of fracture, ranging from the simple type, such as oblique and transverse fractures, to complex fractures. However, literature that investigated its biomechanical analyses to further justify its efficacy is limited. Therefore, this paper aimed to analyse the stability of unilateral external fixator for treating different types of fracture, including the simple oblique, AO32C3 comminuted, and 20 mm gap transverse fracture. These fractures were reconstructed at the distal diaphysis of the femoral bone and computationally analysed through the finite element method under the stance phase condition. Findings showed a decrease in the fixation stiffness in large gap fracture (645.2 Nmm-1 for oblique and comminuted, while 23.4 Nmm-1 for the gap fracture), which resulted in higher displacement, IFM and stress distribution at the pin bone interface. These unfavourable conditions could consequently increase the risk of delayed union, pin loosening and infection, as well as implant failure. Nevertheless, the stress observed on the fracture surfaces was relatively low and in controlled amount, indicating that bone unity is still allowable in all models. Briefly, the unilateral fixation may provide desirable results in smaller fracture gap, but its usage in larger gap fracture might be alarming. These findings could serve as a guide and insight for surgeons and researchers, especially on the biomechanical stability of fixation in different fracture types and how will it affect bone unity.
Keywords: External fixator; Femur; Finite element analysis; Fracture healing; Pin tract infection.
© 2024 The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no known competing financial interests or personal relationships that could have appeared to influence the work reported in this paper.
Figures




Similar articles
-
A finite element study: Finding the best configuration between unilateral, hybrid, and ilizarov in terms of biomechanical point of view.Injury. 2020 Nov;51(11):2474-2478. doi: 10.1016/j.injury.2020.08.001. Epub 2020 Aug 2. Injury. 2020. PMID: 32798038
-
Comparison between external locking plate fixation and conventional external fixation for extraarticular proximal tibial fractures: a finite element analysis.J Orthop Surg Res. 2022 Jan 11;17(1):16. doi: 10.1186/s13018-021-02907-3. J Orthop Surg Res. 2022. PMID: 35016716 Free PMC article.
-
Mechanical stability study of three techniques used in the fixation of transverse and oblique metaphyseal-diaphyseal junction fractures of the distal humerus in children: a finite element analysis.J Orthop Surg Res. 2020 Jan 31;15(1):34. doi: 10.1186/s13018-020-1564-4. J Orthop Surg Res. 2020. PMID: 32020882 Free PMC article.
-
A theoretical analysis and finite element simulation of fixator-bone system stiffness on healing progression.J Appl Biomater Funct Mater. 2018 Jul;16(3):115-125. doi: 10.1177/2280800017750357. Epub 2018 Mar 27. J Appl Biomater Funct Mater. 2018. PMID: 29582693
-
Fractures of the femur.Vet Clin North Am Small Anim Pract. 1992 Jan;22(1):149-59. doi: 10.1016/s0195-5616(92)50010-9. Vet Clin North Am Small Anim Pract. 1992. PMID: 1539422 Review.
Cited by
-
Elbow stiffness due to malunited capitellum fracture: A case report and the role of 3D printing in surgical management.Int J Surg Case Rep. 2024 Nov;124:110398. doi: 10.1016/j.ijscr.2024.110398. Epub 2024 Sep 30. Int J Surg Case Rep. 2024. PMID: 39395254 Free PMC article.
-
Heparin-binding of the human chitinase-like protein YKL-40 is allosterically modified by chitin oligosaccharides.Biochem Biophys Rep. 2024 Dec 24;41:101908. doi: 10.1016/j.bbrep.2024.101908. eCollection 2025 Mar. Biochem Biophys Rep. 2024. PMID: 39811191 Free PMC article.
-
Finite element analysis and clinical evaluation of cross locking external fixator configuration for distal third tibia fracture.Sci Rep. 2025 Apr 17;15(1):13310. doi: 10.1038/s41598-025-97090-4. Sci Rep. 2025. PMID: 40247025 Free PMC article.
-
Finite element analysis of the stability of tibiofibular fractures treated with various combinations of external fixators.BMC Musculoskelet Disord. 2025 Mar 27;26(1):304. doi: 10.1186/s12891-025-08530-1. BMC Musculoskelet Disord. 2025. PMID: 40148854 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Suaimi M.K.A., Ab Rashid A.M., Nasution A.K., Hong Seng G., Abdul Kadir M.R., Ramlee M.H. Biomechanical evaluation of locking compression plate (LCP) versus Dynamic compression plate (DCP): a finite element analysis. J. Teknol. 2022;84:125–131. doi: 10.11113/jurnalteknologi.v84.16687. - DOI
-
- Schmitt D., Halvachizadeh S., Steinemann R., Jensen K.O., Berk T., Neuhaus V., Mica L., Pfeifer R., Pape H.C., Sprengel K. Trauma team activation: which surgical capability is immediately required in polytrauma? A retrospective, monocentric analysis of emergency procedures performed on 751 severely injured patients. J. Clin. Med. 2021;10:4335. doi: 10.3390/jcm10194335. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Manon J., Pletser V., Saint-Guillain M., Vanderdonckt J., Wain C., Jacobs J., Comein A., Drouet S., Meert J., Sanchez Casla I.J., Cartiaux O., Cornu O. An easy-to-use external fixator for all hostile environments, from space to war medicine: is it meant for everyone's hands? J. Clin. Med. 2023;12:4764. doi: 10.3390/jcm12144764. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

