Pericapsular nerve group block versus fascia iliaca block for perioperative analgesia in hip fracture surgery: a prospective randomized trial
- PMID: 38405096
- PMCID: PMC10891367
- DOI: 10.11604/pamj.2023.46.93.41117
Pericapsular nerve group block versus fascia iliaca block for perioperative analgesia in hip fracture surgery: a prospective randomized trial
Abstract
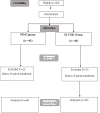
The aim of our study was to evaluate the efficacy of the pericapsular nerve group block (PENG) versus the supra-inguinal fascia iliaca compartment block (SI-FICB) to improve analgesia during positioning for spinal anesthesia (SA) for hip fracture surgery. We conducted a prospective randomized clinical trial involving patients who will undergo hip fracture surgery under SA and randomized into two groups: the PENG group: patients who received PENG block with 10 ml of 0.25% bupivacaine and 10 ml of 2% lidocaine and the SI-FICB group: patients who received SI-FICB block with the same solution. Our primary outcome was the Visual Analogue Scale (VAS) score at positioning for SA. Secondary outcomes were VAS after the block, the ease of spinal positioning (EOSP), the time to perform the block, the postoperative morphine consumption, and the VAS score at the 3rd, 6th, 12th, and 24th postoperative hours. Eighty-nine patients were enrolled and randomized into two groups: 44 in the PENG group and 45 in the SI-FICB group. The time of block performance was comparable in both groups (p = 0.195). There was a significant decrease in pain scores in the 2 groups, 20 min after the blocks at rest and while positioning for SA. PENG block provided better analgesia than SI-FICB block at positioning (P=0.046) with no significant difference in the ease of positioning (p=0.328). The morphine consumption was comparable in the 2 groups (p = 0.842). There was no significant difference in VAS scores at the 3rd, 6th, 12th, and 24th postoperative hours with p respectively 0.061, 0.767, 0.198, and 0.130. Both PENG and SI-FICB blocks provided adequate perioperative analgesia with the superiority of the PENG block in the sitting position for SA.
Keywords: Pericapsular nerve group block (PENG); hip fracture surgery; perioperative analgesia; supra-inguinal fascia iliaca compartment block (SI-FICB).
Copyright: Mariem Keskes et al.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures
References
-
- Parker MJ. Current concepts in the treatment of hip fracture. Z Gerontol Geriatr. 2001;34(1):74–7. - PubMed
-
- Cooper C, Campion G, Melton LJ., 3rd Hip fractures in the elderly: a world-wide projection. Osteoporos Int. 1992;2(6):285–9. - PubMed
-
- Haleem S, Lutchman L, Mayahi R, Grice JE, Parker MJ. Mortality following hip fracture: trends and geographical variations over the last 40 years. Injury. 2008;39(10):1157–63. - PubMed
-
- Neuman MD, Feng R, Carson JL, Gaskins LJ, Dillane D, Sessler DI, et al. Spinal Anesthesia or General Anesthesia for Hip Surgery in Older Adults. N Engl J Med. 2021 Nov 25;385(22):2025–2035. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous