Evaluation of the efficacy of a sunscreen containing ultra-long UVA1 and other UVR broad-spectrum filters on skin barrier protection and melanin content reduction in Chinese adults: A single-center study
- PMID: 38405170
- PMCID: PMC10884559
- DOI: 10.1002/hsr2.1923
Evaluation of the efficacy of a sunscreen containing ultra-long UVA1 and other UVR broad-spectrum filters on skin barrier protection and melanin content reduction in Chinese adults: A single-center study
Abstract
Background and aims: The protection for ultra-long UVA1 is lacked in the market, posing potential damage from ultra-long UVA1 irradiation. The study aims to evaluate the efficacy of a sunscreen containing multiple components, especially Mexoryl® 400 for improving skin barrier function and reducing melanin content.
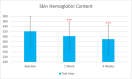
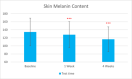
Methods: This single-center study included adults with sensitive and normal skin in China in November 2022. Participants received the test sunscreen for 4 weeks. Melanin and hemoglobin content, sebum secretion skin hydration, and trans-epidermal water loss were evaluated at T0d, T7d, and T28d. The self-assessment was done at T15min, T7d, and T28d.
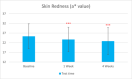
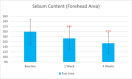
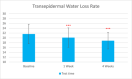
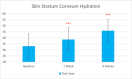
Results: Sixty participants were included, including 30 self-claimed sensitive skin in the sunscreen group. The sunscreen demonstrated significant improvements in skin parameters. Skin redness reduced by 9.84% at T28d, sebum content in the forehead area decreased by 22.70% at T28d, and skin stratum corneum hydration increased by 38.44% at T28d, p < 0.001 respectively. Most notably, skin melanin content significantly reduced by 13.49% after 4 weeks' usage (p < 0.001). No adverse reactions were reported in either group.
Conclusions: The study sunscreen improved the skin condition by decreasing the melanin content, regulating skin barrier function, and achieving a balance of skin hydration and sebum secretion.
Keywords: Mexoryl® 400; UVA1; Vitamin E; skin barrier; skin pigmentation.
© 2024 L'Oréal China. Health Science Reports published by Wiley Periodicals LLC.
Conflict of interest statement
The author(s) are affiliated with L'Oreal (China) and L'Oreal R&I. The remaining author declare no conflict of interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Efficacy and safety of a facial serum and a mask containing salicylic acid and lipohydroxy acid in acne management: A randomized controlled trial.J Cosmet Dermatol. 2023 Sep;22(9):2502-2511. doi: 10.1111/jocd.15746. Epub 2023 Mar 31. J Cosmet Dermatol. 2023. PMID: 36999489 Clinical Trial.
-
Efficacy of ceramide-containing sunscreen on skin barrier.J Cosmet Dermatol. 2024 Feb;23(2):525-528. doi: 10.1111/jocd.15977. Epub 2023 Aug 29. J Cosmet Dermatol. 2024. PMID: 37641585
-
The Effect of Sunscreens on the Skin Barrier.Life (Basel). 2022 Dec 12;12(12):2083. doi: 10.3390/life12122083. Life (Basel). 2022. PMID: 36556448 Free PMC article.
-
Natural components in sunscreens: Topical formulations with sun protection factor (SPF).Biomed Pharmacother. 2021 Feb;134:111161. doi: 10.1016/j.biopha.2020.111161. Epub 2020 Dec 24. Biomed Pharmacother. 2021. PMID: 33360043 Review.
-
Sunscreens containing the broad-spectrum UVA absorber, Mexoryl SX, prevent the cutaneous detrimental effects of UV exposure: a review of clinical study results.Photodermatol Photoimmunol Photomed. 2008 Aug;24(4):164-74. doi: 10.1111/j.1600-0781.2008.00365.x. Photodermatol Photoimmunol Photomed. 2008. PMID: 18717957 Review.
References
-
- Battie C, Verschoore M. Cutaneous solar ultraviolet exposure and clinical aspects of photodamage. Indian J Dermatol Venereol Leprol. 2012;78(suppl 1):9. - PubMed
-
- Marionnet C, Nouveau S, Hourblin V, et al. UVA1‐Induced skin darkening is associated with molecular changes even in highly pigmented skin individuals. J Invest Dermatol. 2017;137:1184‐1187. - PubMed
-
- Bak H, Hong S, Jeong SK, et al. Altered epidermal lipid layers induced by long‐term exposure to suberythemal‐dose ultraviolet. Int J Dermatol. 2011;50(7):832‐837. - PubMed
-
- Grimes PE. Management of hyperpigmentation in darker racial ethnic groups. Semin Cutan Med Surg. 2009;28(2):77‐85. - PubMed
-
- Seité S, Fourtanier A, Moyal D, Young AR. Photodamage to human skin by suberythemal exposure to solar ultraviolet radiation can be attenuated by sunscreens: a review. Br J Dermatol. 2010;163(5):903‐914. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

