Risk factors for urinary tract infection in geriatric hip fracture patients: a systematic review and meta-analysis
- PMID: 38405191
- PMCID: PMC10884186
- DOI: 10.3389/fmed.2024.1360058
Risk factors for urinary tract infection in geriatric hip fracture patients: a systematic review and meta-analysis
Abstract
Background: Urinary tract infection (UTI) is a prevalent and consequential complication in hip fracture patients, leading to significant disability and heightened healthcare expenditures. Consequently, there is a critical need for a comprehensive systematic review to identify risk factors and establish early and effective preventive measures.
Methods: A comprehensive search was performed across the PubMed, Cochrane, Embase, Web of Science, and Scopus databases (up to August 31, 2023). Article screening, data extraction, and quality assessment were independently completed by two reviewers.
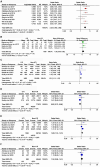
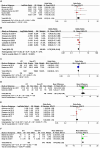
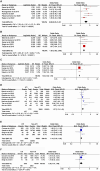
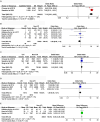
Results: Forty-four studies were eligible for inclusion, yielding an overall incidence rate of 11% (95% CI: 8%-14%). Our pooled analysis revealed 18 significant risk factors, including being female (OR = 2.23, 95% CI: 1.89-2.63), advanced age (MD = 1.35, 95% CI: 0.04-2.66), obesity (OR = 1.21, 95% CI: 1.11-1.31), catheterization (OR = 3.8, 95% CI: 2.29-6.32), blood transfusion (OR = 1.39, 95% CI: 1.21-1.58), American Society of Anesthesiologists ≥III (OR = 1.28, 95% CI: 1.18-1.40), general anesthesia (OR = 1.26, 95% CI: 1.11-1.43), intertrochanteric fracture (OR = 1.25, 95% CI: 1.01-1.54), hemiarthroplasty (OR = 1.43, 95% CI: 1.19-1.69), prolonged length of hospital stay (MD = 1.44, 95% CI: 0.66-2.23), delirium (OR = 2.66, 95% CI: 2.05-3.47), dementia (OR = 1.82, 95% CI: 1.62-2.06), Parkinson's disease (OR = 1.53, 95% CI: 1.46-1.61), diabetes (OR = 1.27, 95% CI: 1.13-1.43), hypertension (OR = 1.14, 95% CI: 1.03-1.26), congestive heart failure (OR = 1.35, 95% CI: 1.10-1.66), history of sepsis (OR = 7.13, 95% CI: 5.51-9.22), and chronic steroid use (OR = 1.29, 95% CI: 1.06-1.57).
Conclusion: Our study identifies numerous risk factors strongly associated with UTI, offering compelling evidence and actionable strategies for improving clinical prediction, enabling early intervention, and facilitating targeted UTI management.
Systematic review registration: identifier [CRD42023459600], https://www.crd.york.ac.uk/PROSPERO/display_record.php?RecordID=459600.
Keywords: UTI; hip fracture; meta-analysis; risk factors; urinary tract infection.
Copyright © 2024 Wang, Yao, Tang, Li, Sun and Ding.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Incidence, risk factors and clinical implications of postoperative urinary tract infection in geriatric hip fractures.Injury. 2022 Jun;53(6):2158-2162. doi: 10.1016/j.injury.2022.03.012. Epub 2022 Mar 8. Injury. 2022. PMID: 35339273
-
Community-based care for the specialized management of heart failure: an evidence-based analysis.Ont Health Technol Assess Ser. 2009;9(17):1-42. Epub 2009 Nov 1. Ont Health Technol Assess Ser. 2009. PMID: 23074521 Free PMC article.
-
Incidence of delirium after non-cardiac surgery in the Chinese elderly population: a systematic review and meta-analysis.Front Aging Neurosci. 2023 Jun 29;15:1188967. doi: 10.3389/fnagi.2023.1188967. eCollection 2023. Front Aging Neurosci. 2023. PMID: 37455941 Free PMC article.
-
Neuraxial versus general anesthesia in elderly patients undergoing hip fracture surgery and the incidence of postoperative delirium: a systematic review and stratified meta-analysis.BMC Anesthesiol. 2023 Jul 22;23(1):250. doi: 10.1186/s12871-023-02196-9. BMC Anesthesiol. 2023. PMID: 37481517 Free PMC article.
-
Urinary tract infection (UTI) at time of geriatric hip fracture surgery increases the risk of experiencing adverse 30-day outcomes.J Clin Orthop Trauma. 2019 Jul-Aug;10(4):774-778. doi: 10.1016/j.jcot.2018.07.014. Epub 2018 Jul 19. J Clin Orthop Trauma. 2019. PMID: 31316253 Free PMC article.
Cited by
-
Factors associated with the occurrence of postoperative infection of intertrochanteric fracture of the femur and its prediction model creation and validation.Medicine (Baltimore). 2025 Jul 18;104(29):e43397. doi: 10.1097/MD.0000000000043397. Medicine (Baltimore). 2025. PMID: 40696658 Free PMC article.
References
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

