Digital Twin Fundamentals of mRNA In Vitro Transcription in Variable Scale Toward Autonomous Operation
- PMID: 38405539
- PMCID: PMC10882708
- DOI: 10.1021/acsomega.3c08732
Digital Twin Fundamentals of mRNA In Vitro Transcription in Variable Scale Toward Autonomous Operation
Abstract
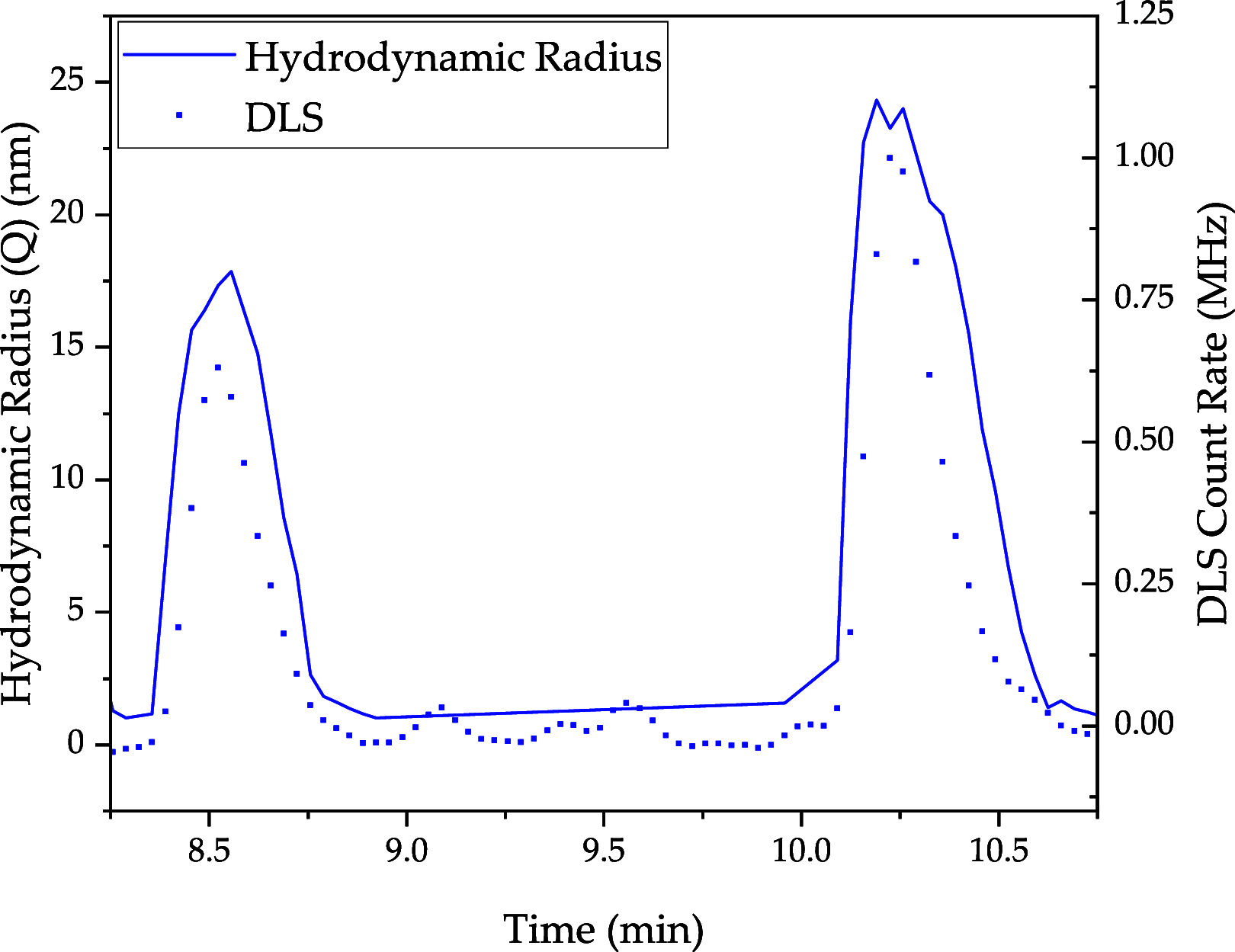
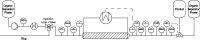
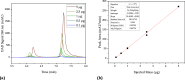
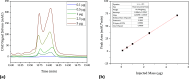
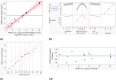
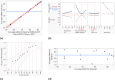
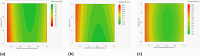
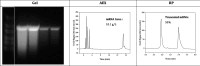
The COVID-19 pandemic caused the rapid development of mRNA (messenger ribonucleic acid) vaccines and new RNA-based therapeutic methods. However, the approval rate for candidates has the potential to be increased, with a significant number failing so far due to efficacy, safety, and manufacturing deficiencies, hindering equitable vaccine distribution during pandemics. This study focuses on optimizing the production of mRNA, a critical component of mRNA-based vaccines, using a scalable machine by investigating the key mechanisms of mRNA in vitro transcription. First, kinetic parameters for the mRNA production process were determined. The validity of the determination and the robustness of the model are demonstrated by predicting different reactions with and without substrate limitations as well as different transcripts. The optimized reaction conditions, including temperature, urea concentration, and concentration of reaction-enhancing additives, resulted in a 55% increase in mRNA yield with a 33% reduction in truncated mRNA. Additionally, the feasibility of a segmented flow approach allowed for high-throughput screening (HTS), enabling the production of 20 vaccine candidates within a short time frame, representing a 10-fold increase in productivity, compared to nonsegmented reactions limited by the residence time in the plug flow reactor. The findings presented for the first time here contribute to the development of a fully continuous and efficient manufacturing process for mRNA and other cell and gene therapy drugs/vaccine candidates as presented in our previous work, which discussed the integration of process analytical technologies and predictive process models in a Biopharma 4.0 facility to enable the production of clinical and large-scale doses, ensuring a rapid and resilient supply of critical therapeutics. The results in this study especially highlight that the same machine and equipment can be used for screening and manufacturing different drug candidates in continuous operation. By streamlining production and adhering to quality standards, this approach enhances the industry's ability to respond swiftly to pandemics and public health emergencies, addressing the urgent need for accessible and effective vaccines.
© 2024 The Authors. Published by American Chemical Society.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing financial interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
The Rapid Development and Early Success of Covid 19 Vaccines Have Raised Hopes for Accelerating the Cancer Treatment Mechanism.Arch Razi Inst. 2021 Mar;76(1):1-6. doi: 10.22092/ari.2021.353761.1612. Epub 2021 Mar 1. Arch Razi Inst. 2021. PMID: 33818952 Free PMC article.
-
Current Status and Future Perspectives on MRNA Drug Manufacturing.Mol Pharm. 2022 Apr 4;19(4):1047-1058. doi: 10.1021/acs.molpharmaceut.2c00010. Epub 2022 Mar 3. Mol Pharm. 2022. PMID: 35238565 Review.
-
Anion exchange HPLC monitoring of mRNA in vitro transcription reactions to support mRNA manufacturing process development.Front Mol Biosci. 2024 Mar 7;11:1250833. doi: 10.3389/fmolb.2024.1250833. eCollection 2024. Front Mol Biosci. 2024. PMID: 38516194 Free PMC article.
-
[Standard technical specifications for methacholine chloride (Methacholine) bronchial challenge test (2023)].Zhonghua Jie He He Hu Xi Za Zhi. 2024 Feb 12;47(2):101-119. doi: 10.3760/cma.j.cn112147-20231019-00247. Zhonghua Jie He He Hu Xi Za Zhi. 2024. PMID: 38309959 Chinese.
-
Development of mRNA manufacturing for vaccines and therapeutics: mRNA platform requirements and development of a scalable production process to support early phase clinical trials.Transl Res. 2022 Apr;242:38-55. doi: 10.1016/j.trsl.2021.11.009. Epub 2021 Dec 4. Transl Res. 2022. PMID: 34871810 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Bacteriophage RNA polymerases: catalysts for mRNA vaccines and therapeutics.Front Mol Biosci. 2024 Nov 21;11:1504876. doi: 10.3389/fmolb.2024.1504876. eCollection 2024. Front Mol Biosci. 2024. PMID: 39640848 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Castellanos M. M.; Gressard H.; Li X.; Magagnoli C.; Moriconi A.; Stranges D.; Strodiot L.; Tello Soto M.; Zwierzyna M.; Campa C. CMC Strategies and Advanced Technologies for Vaccine Development to Boost Acceleration and Pandemic Preparedness. Vaccines 2023, 11 (7), 1153.10.3390/vaccines11071153. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
