Microvascularized Fibular Bone Grafting for the Treatment of Mandibular Expansive Osseous Dysplasia - A Case Report
- PMID: 38405551
- PMCID: PMC10883211
- DOI: 10.4103/ams.ams_63_23
Microvascularized Fibular Bone Grafting for the Treatment of Mandibular Expansive Osseous Dysplasia - A Case Report
Abstract
Rationale: Osseous dysplasia (OD) is a benign fibro-osseous lesion classified as periapical, focal or florid with some rare cases being diagnosed as expansive OD.
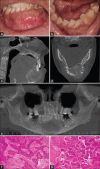
Patient concerns: A 43-year-old female presented with gross mandible expansion and tooth displacement.
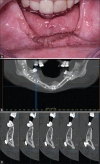
Diagnosis: Imaging scans revealed an expansive lesion in the anterior mandible, with varying opacity in the central region, and other smaller lesions in the region of teeth #37 and #47, consistent with expansive OD.
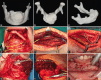
Treatment: Surgical resection followed by immediate reconstruction of the mandibular defect using a microvascularized fibular graft.
Outcomes: The patient had a 4-year follow-up, with adequate mandibular bone continuity, mastication, swallowing, and speaking ability reestablished.
Take-away lessons: Immediate reconstruction after large surgical resection is required as tissues retract over time, hampering late reconstructions. Microvascularized fibular graft aims at adequate and functional rehabilitation with osseointegrated implants and long-term follow-up is needed as florid OD may evolve into expansive OD.
Keywords: Bone dysplasias; case report; florid cemento-osseous dysplasia; mandibular reconstruction; vascular grafting.
Copyright: © 2023 Annals of Maxillofacial Surgery.
Conflict of interest statement
There are no conflicts of interest.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Expansive focal cemento-osseous dysplasia.J Contemp Dent Pract. 2012 Jan 1;13(1):115-8. doi: 10.5005/jp-journals-10024-1105. J Contemp Dent Pract. 2012. PMID: 22430704
-
Florid cemento-osseous dysplasia: A case report.Indian J Dent Res. 2021 Jan-Feb;32(1):134-136. doi: 10.4103/ijdr.IJDR_754_18. Indian J Dent Res. 2021. PMID: 34269253
-
Florid Cemento-osseous Dysplasia Associated with Secondary Infection - A Case Report.Ann Maxillofac Surg. 2023 Jul-Dec;13(2):232-235. doi: 10.4103/ams.ams_49_23. Epub 2023 Sep 26. Ann Maxillofac Surg. 2023. PMID: 38405575 Free PMC article.
-
Associated aneurysmal bone cyst and cemento-osseous dysplasia: a case report and review of the literature.Gen Dent. 2017 Jan-Feb;65(1):28-32. Gen Dent. 2017. PMID: 28068262 Review.
-
Florid cemento-osseous dysplasia: review of an uncommon fibro-osseous lesion of the jaw with important clinical implications.Skeletal Radiol. 2017 May;46(5):581-590. doi: 10.1007/s00256-017-2590-0. Epub 2017 Feb 13. Skeletal Radiol. 2017. PMID: 28194495 Review.
Cited by
-
Florid cemento-osseous dysplasia: A case report and review of literature.Heliyon. 2024 Jun 27;10(14):e33746. doi: 10.1016/j.heliyon.2024.e33746. eCollection 2024 Jul 30. Heliyon. 2024. PMID: 39114015 Free PMC article.
References
-
- El Naggar AK, Chan JC, Grandis JR, Takata T, Slootweg PJ. 4th ed. Lyon: IARC Press; 2017. WHO Classification of Head and Neck Tumors.
-
- Fenerty S, Shaw W, Verma R, Syed AB, Kuklani R, Yang J, et al. Florid cemento-osseous dysplasia: Review of an uncommon fibro-osseous lesion of the jaw with important clinical implications. Skeletal Radiol. 2017;46:581–90. - PubMed
-
- Noffke CE, Raubenheimer EJ. Expansive osseous dysplasia: Report of 9 lesions in an African population sample and a review of the literature. Oral Surg Oral Med Oral Pathol Oral Radiol Endod. 2011;111:e35–41. - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
