Surgical Rehabilitation of a Continuous Orbital and Maxillary Defect from Rhino-Orbital Mucormycosis Utilising Digital Technology - A Case Report
- PMID: 38405554
- PMCID: PMC10883209
- DOI: 10.4103/ams.ams_54_23
Surgical Rehabilitation of a Continuous Orbital and Maxillary Defect from Rhino-Orbital Mucormycosis Utilising Digital Technology - A Case Report
Abstract
Rationale: COVID-19 has led to a resurgence in cases of mucormycosis, especially the rhino-orbital form affecting the oral cavity, nasal, orbital and cerebral regions.
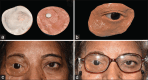
Patient concerns: The surgical treatment in this patient led to the exenteration of orbital contents and segmental maxillectomy of the affected side leading to facial disfigurement and inability to masticate.
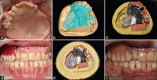
Diagnosis: A combined mucormycosis-associated oro-orbital defect was present leading to a communication between oral and orbital cavities.
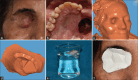
Treatment: Rehabilitation utilising digital technology for removable prosthesis was planned for the combined orbital and oral defect.
Outcomes: The independent intraoral and orbital prosthesis reduced the mobility of the orbital prosthesis while performing functional movements. The advancements in digital technology led to the convenient and resilient fabrication of prostheses for large facial defects.
Take-away lessons: The prosthetic rehabilitation of a continuous orbital and oral defect with a hybrid of both digital and conventional means provided an aesthetic, feasible and financially sound solution to the patient.
Keywords: Hollow obturator; orbital exenteration; segmental maxillectomy; three-dimensional printing.
Copyright: © 2023 Annals of Maxillofacial Surgery.
Conflict of interest statement
There are no conflicts of interest.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Magnet-Retained closed bulb hollow obturator and orbital prosthesis for patient with maxillectomy and orbital exenteration following COVID-Associated mucormycosis.Niger Postgrad Med J. 2023 Apr-Jun;30(2):175-179. doi: 10.4103/npmj.npmj_337_22. Niger Postgrad Med J. 2023. PMID: 37148122
-
Prosthetic Rehabilitation Following Segmental Maxillectomy Confluent with an Orbital Defect Using a Hollow Orbital Prosthesis Retained Magnetically with an Obturator: A Case Report.J West Afr Coll Surg. 2023 Jan-Mar;13(1):98-102. doi: 10.4103/jwas.jwas_234_22. Epub 2023 Jan 18. J West Afr Coll Surg. 2023. PMID: 36923806 Free PMC article.
-
Prosthetic Rehabilitation of a Post-mucormycosis Maxillectomy Defect Using a Maxillary Hollow Obturator and Complete Denture: A Case Report.Cureus. 2025 May 11;17(5):e83881. doi: 10.7759/cureus.83881. eCollection 2025 May. Cureus. 2025. PMID: 40497196 Free PMC article.
-
The rising challenge of mucormycosis for maxillofacial prosthodontists in the Covid-19 pandemic: A literature review.J Prosthodont Res. 2022 Jul 30;66(3):395-401. doi: 10.2186/jpr.JPR_D_21_00264. Epub 2022 Mar 11. J Prosthodont Res. 2022. PMID: 35283402 Review.
-
A systematic review of the computerized tools and digital techniques applied to fabricate nasal, auricular, orbital and ocular prostheses for facial defect rehabilitation.J Stomatol Oral Maxillofac Surg. 2020 Jun;121(3):268-277. doi: 10.1016/j.jormas.2019.10.003. Epub 2019 Oct 11. J Stomatol Oral Maxillofac Surg. 2020. PMID: 31610244
References
-
- Martel A, Baillif S, Nahon-Esteve S, Gastaud L, Bertolotto C, Lassalle S, et al. Orbital exenteration: An updated review with perspectives. Surv Ophthalmol. 2021;66:856–76. - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
