Florid Cemento-osseous Dysplasia Associated with Secondary Infection - A Case Report
- PMID: 38405575
- PMCID: PMC10883215
- DOI: 10.4103/ams.ams_49_23
Florid Cemento-osseous Dysplasia Associated with Secondary Infection - A Case Report
Abstract
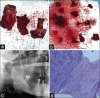
Rationale: The term cemento-osseous dysplasia (COD) refers to a bony fibro-osseous lesion, in which fibrous tissue and cementum-like tissue replace normal bone. There are three types of COD: periapical, focal and florid. The condition is usually asymptomatic and treatment is unnecessary; however, a secondary infection could occur, which requires treatment.
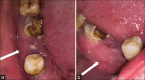
Patient concern: A 58-year-old female patient presented with symptoms in the mandibular posterior region of the right jaw for six months.
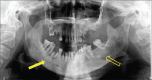
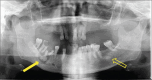
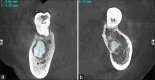
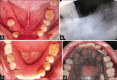
Diagnosis: Infected florid COD (FCOD).
Treatment: A pre-operative antibiotic, followed by extraction of non-restorable teeth, debridement of the infected tissue and necrotic bone removal.
Outcome: The patient was followed for one year, during which all previously reported signs and symptoms were resolved.
Take-away lessons: Early lesion detection is essential. Treatment depends on the presence or absence of clinical and radiographic manifestations. The current case was treated surgically to minimise complications.
Keywords: Cemento-osseous dysplasia; florid; focal; infection; periapical.
Copyright: © 2023 Annals of Maxillofacial Surgery.
Conflict of interest statement
There are no conflicts of interest.
Figures
References
-
- El-Naggar AK, Chan JK, Grandis JR. Geneva, Switzerland: IARC Press, WHO Press, World Health Organization; 2017. WHO Classification of Head and Neck Tumours.
-
- Fokam ST, Kwedi GK, Messanga CB. Infected florid cemento-osseous dysplasia: About one clinical observation. Adv Oral Maxillofac Surg. 2022;7:100298.
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
