Case Report: In situ pulmonary artery thrombosis in a 12-year-old girl classified as systemic lupus erythematosus
- PMID: 38405595
- PMCID: PMC10885351
- DOI: 10.3389/fped.2024.1341188
Case Report: In situ pulmonary artery thrombosis in a 12-year-old girl classified as systemic lupus erythematosus
Abstract
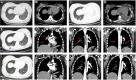
In situ pulmonary artery thrombosis (ISPAT) is a relatively rare but potentially life-threatening complication of systemic lupus erythematosus (SLE) in children. We report the case of a 12-year-old girl who presented with fever, chest pain, and dyspnea. Immune thrombocytopenia was identified due to purpura and menorrhagia 3 months before presentation with a lowest platelet count of 12 × 109/L. The sudden onset of fever, chest pain, and dyspnea were misdiagnosed as hyperinflammatory responses caused by pneumonia; these symptoms ameliorated with glucocorticoid and antibiotic treatment. The reappearance of symptoms after dose reduction of glucocorticoids and the observation of bloody bronchoalveolar lavage fluid necessitated further evaluation. Pulmonary artery thrombosis/embolism was identified using computed tomography pulmonary angiography and high D-dimer quantitative level of 4,118 μg/L (normal <252 μg/L). Ultrasonography of the deep and superficial veins of both lower limbs and renal veins revealed no thrombosis, suggesting the diagnosis of ISPAT. Further etiological evaluation revealed positive antinuclear antibodies, lupus anticoagulant, and anti-SSA antibodies, confirming SLE. Repeated normal urine analysis indicated that lupus nephritis was unlikely. Further, the negative anticardiolipin and anti-β2 glycoprotein antibodies and temporary positive lupus anticoagulant suggested that antiphospholipid syndrome was unlikely. The patient received anticoagulants, glucocorticoids, hydroxychloroquine, and mycophenolate therapy. Her symptoms gradually improved, and she was discharged. At the 1-month follow-up, the thrombosis had resolved. During the 1-year follow-up, her condition remained well without SLE relapse. Our experience with this case emphasizes searching for SLE in the case of ISPAT and pulmonary hemorrhages. ISPAT can occur in children with SLE and may be caused by hyperinflammatory response during SLE flare.
Keywords: antiphospholipid syndrome; child; in situ pulmonary artery thrombosis; pulmonary embolism; systemic lupus erythematosus.
© 2024 Feng, Chen, Dai and Shang.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Cerebral Venous Sinus Thrombosis in Systemic Lupus Erythematosus.Acta Med Indones. 2018 Oct;50(4):343-345. Acta Med Indones. 2018. PMID: 30631001
-
[Adrenal hemorrhage in a patient with systemic lupus erythematosus].Beijing Da Xue Xue Bao Yi Xue Ban. 2019 Dec 18;51(6):1178-1181. doi: 10.19723/j.issn.1671-167X.2019.06.036. Beijing Da Xue Xue Bao Yi Xue Ban. 2019. PMID: 31848526 Free PMC article. Chinese.
-
Catastrophic Anti-Phospholipid Syndrome in Systemic Lupus Erythematosus: A Tsunami in the Ocean.J Assoc Physicians India. 2022 Apr;70(4):11-12. J Assoc Physicians India. 2022. PMID: 35443434
-
Shrinking lung syndrome treated with rituximab in pediatric systemic lupus erythematosus: a case report and review of the literature.Pediatr Rheumatol Online J. 2021 Jan 6;19(1):7. doi: 10.1186/s12969-020-00491-0. Pediatr Rheumatol Online J. 2021. PMID: 33407629 Free PMC article. Review.
-
An Antiphospholipid Antibody Profile as a Biomarker for Thrombophilia in Systemic Lupus Erythematosus.Biomolecules. 2023 Mar 30;13(4):617. doi: 10.3390/biom13040617. Biomolecules. 2023. PMID: 37189365 Free PMC article. Review.
References
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials

