Treatment of Post-stroke Dysphagia With Interferential Current: Three Case Reports and a Review of the Literature
- PMID: 38405658
- PMCID: PMC10894016
- DOI: 10.7759/cureus.54806
Treatment of Post-stroke Dysphagia With Interferential Current: Three Case Reports and a Review of the Literature
Abstract
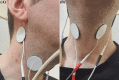
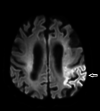
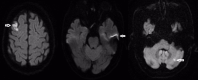
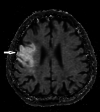
Stroke is damage to the central nervous system due to vascular pathology. Stroke causes many complications. One of the most important of these complications is dysphagia. Dysphagia is a major cause of morbidity and mortality. In recent years, the benefits of using interferential current (IFC) stimulation in the treatment of dysphagia due to various etiologies have been demonstrated. However, there are significant gaps in the literature regarding patient populations, treatment procedures, and evaluation of treatment response. Here, we report the treatment of three cases of dysphagia after ischemic stroke with IFC stimulation and review the current literature. The patients had no previous treatment for dysphagia and were using only compensatory methods. This case report highlights the benefit of IFC stimulation in the treatment of post-stroke dysphagia both clinically and videofluoroscopically. It should be kept in mind that IFC stimulation may be an important alternative in the treatment of post-stroke dysphagia.
Keywords: dysphagia; interferential current; stimulation; stroke; swallow; therapy.
Copyright © 2024, Alyanak et al.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors have declared that no competing interests exist.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Effects of Active Interferential Current Stimulation on Swallowing Function in Patients with Dysphagia: A Cross-Sectional Study of Interferential Current Stimulation on Swallowing Function in Patients with Dysphagia: A Cross-Sectional Study.Dysphagia. 2025 Jun 17. doi: 10.1007/s00455-025-10853-z. Online ahead of print. Dysphagia. 2025. PMID: 40528011
-
The Effect of Sensory Level Versus Motor Level Electrical Stimulation of Pharyngeal Muscles in Acute Stroke Patients with Dysphagia: A Randomized Trial.Dysphagia. 2023 Jun;38(3):943-953. doi: 10.1007/s00455-022-10520-7. Epub 2022 Sep 20. Dysphagia. 2023. PMID: 36127447 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial.
-
Efficacy of interferential current transcutaneous electrical sensory stimulation through the neck skin for treating dysphagia in children with disabilities: A case series.SAGE Open Med Case Rep. 2023 Jan 17;11:2050313X221149527. doi: 10.1177/2050313X221149527. eCollection 2023. SAGE Open Med Case Rep. 2023. PMID: 36686208 Free PMC article.
-
Analgesic Effects of Interferential Current Therapy: A Narrative Review.Medicina (Kaunas). 2022 Jan 17;58(1):141. doi: 10.3390/medicina58010141. Medicina (Kaunas). 2022. PMID: 35056448 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The role of interferential current electrical stimulation in pediatric urology: A systematic review of randomized controlled trials.Surg Neurol Int. 2023 Nov 24;14:404. doi: 10.25259/SNI_615_2023. eCollection 2023. Surg Neurol Int. 2023. PMID: 38053700 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Effects of Active Interferential Current Stimulation on Swallowing Function in Patients with Dysphagia: A Cross-Sectional Study of Interferential Current Stimulation on Swallowing Function in Patients with Dysphagia: A Cross-Sectional Study.Dysphagia. 2025 Jun 17. doi: 10.1007/s00455-025-10853-z. Online ahead of print. Dysphagia. 2025. PMID: 40528011
References
-
- Best practice recommendations for stroke patients with dysphagia: a Delphi-based consensus study of experts in Turkey-part I: management, diagnosis, and follow-up. Umay E, Eyigor S, Ertekin C, et al. Dysphagia. 2022;37:217–236. - PubMed
-
- Transcutaneous electrical stimulation versus traditional dysphagia therapy: a nonconcurrent cohort study. Blumenfeld L, Hahn Y, Lepage A, Leonard R, Belafsky PC. Otolaryngol Head Neck Surg. 2006;135:754–757. - PubMed
-
- Dysphagia after stroke: incidence, diagnosis, and pulmonary complications. Martino R, Foley N, Bhogal S, Diamant N, Speechley M, Teasell R. Stroke. 2005;36:2756–2763. - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
