This is a preprint.
Mechanisms of Epigenomic and Functional Convergence Between Glucocorticoid- and IL4-Driven Macrophage Programming
- PMID: 38405750
- PMCID: PMC10888924
- DOI: 10.1101/2024.02.16.580560
Mechanisms of Epigenomic and Functional Convergence Between Glucocorticoid- and IL4-Driven Macrophage Programming
Update in
-
Mechanisms of epigenomic and functional convergence between glucocorticoid- and IL4-driven macrophage programming.Nat Commun. 2024 Oct 18;15(1):9000. doi: 10.1038/s41467-024-52942-x. Nat Commun. 2024. PMID: 39424780 Free PMC article.
Abstract
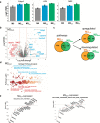
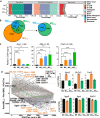
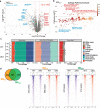
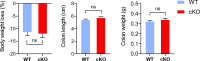
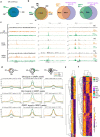
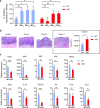
Macrophages adopt distinct phenotypes in response to environmental cues, with type-2 cytokine interleukin-4 promoting a tissue-repair homeostatic state (M2IL4). Glucocorticoids, widely used anti-inflammatory therapeutics, reportedly impart a similar phenotype (M2GC), but how such disparate pathways may functionally converge is unknown. We show using integrative functional genomics that M2IL4 and M2GC transcriptomes share a striking overlap mirrored by a shift in chromatin landscape in both common and signal-specific gene subsets. This core homeostatic program is enacted by transcriptional effectors KLF4 and the GC receptor, whose genome-wide occupancy and actions are integrated in a stimulus-specific manner by the nuclear receptor cofactor GRIP1. Indeed, many of the M2IL4:M2GC-shared transcriptomic changes were GRIP1-dependent. Consistently, GRIP1 loss attenuated phagocytic activity of both populations in vitro and macrophage tissue-repair properties in the murine colitis model in vivo. These findings provide a mechanistic framework for homeostatic macrophage programming by distinct signals, to better inform anti-inflammatory drug design.
Keywords: Homeostatic macrophage programming; chromatin and epigenomics; enhancer landscape; glucocorticoid receptor; kruppel-like factor 4; tissue repair and inflammation; transcriptional regulation.
Figures







References
Publication types
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous
