Massive Pulmonary Embolism Related to a Patient With Heart Failure Secondary to Stress Cardiomyopathy: A Case Report
- PMID: 38406044
- PMCID: PMC10894014
- DOI: 10.7759/cureus.52985
Massive Pulmonary Embolism Related to a Patient With Heart Failure Secondary to Stress Cardiomyopathy: A Case Report
Abstract
Venous thromboembolism (VTE) is a common disease, which includes deep venous thrombosis (DVT) and pulmonary embolism (PE). It is the third most common cardiovascular disorder, affecting predominantly the male elderly population. Stress cardiomyopathy (SC) is a transitorily cardiovascular condition produced after an emotional or physical trigger, and it features signs and symptoms of acute coronary syndrome. Its pathophysiological mechanisms remain unclear, and SC has also been related to critical complications such as heart failure, arrhythmias, left ventricular outflow obstruction, and thromboembolic events. This case report highlights the association of PE and SC that might play a pathophysiological role.
Keywords: pulmonary and cardiac pathophysiology; pulmonary embolism (pe); rare case report; takotsubo cardiomyopathy (ttc); venous thromboembolism (vte).
Copyright © 2024, Pimentel-Esparza et al.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors have declared that no competing interests exist.
Figures

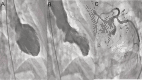
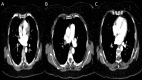
Similar articles
-
The Prevalence of Symptomatic Deep Venous Thrombosis and Pulmonary Embolism After Anterior Cruciate Ligament Reconstruction.Am J Sports Med. 2015 Nov;43(11):2714-9. doi: 10.1177/0363546515601970. Epub 2015 Sep 21. Am J Sports Med. 2015. PMID: 26391861
-
COVID-19-Induced Takotsubo Cardiomyopathy With Concomitant Pulmonary Embolism.Cureus. 2021 Oct 11;13(10):e18693. doi: 10.7759/cureus.18693. eCollection 2021 Oct. Cureus. 2021. PMID: 34659930 Free PMC article.
-
Massive Fatal Pulmonary Embolism While on Therapeutic Heparin Drip.J Investig Med High Impact Case Rep. 2020 Jan-Dec;8:2324709620914787. doi: 10.1177/2324709620914787. J Investig Med High Impact Case Rep. 2020. PMID: 32208868 Free PMC article.
-
Pulmonary Embolism.Med Clin North Am. 2019 May;103(3):549-564. doi: 10.1016/j.mcna.2018.12.013. Med Clin North Am. 2019. PMID: 30955521 Review.
-
Risk of recurrent venous thromboembolism after acute pulmonary embolism: Role of residual pulmonary obstruction and persistent right ventricular dysfunction. A meta-analysis.J Thromb Haemost. 2019 Aug;17(8):1217-1228. doi: 10.1111/jth.14477. Epub 2019 Jun 4. J Thromb Haemost. 2019. PMID: 31063646 Review.
References
-
- Epidemiology and incidence: the scope of the problem and risk factors for development of venous thromboembolism. Stein PD, Matta F. Clin Chest Med. 2010;31:611–628. - PubMed
-
- Pulmonary embolism and deep vein thrombosis: similar but different. Wenger N, Sebastian T, Engelberger RP, Kucher N, Spirk D. Thromb Res. 2021;206:88–98. - PubMed
-
- 2019 ESC Guidelines for the diagnosis and management of acute pulmonary embolism developed in collaboration with the European Respiratory Society (ERS) Konstantinides SV, Meyer G, Becattini C, et al. Eur Heart J. 2020;41:543–603. - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
