Commercially Pure Titanium Implants With Selenium and Hyaluronic Acid Coating for Dental Applications
- PMID: 38406106
- PMCID: PMC10893994
- DOI: 10.7759/cureus.52984
Commercially Pure Titanium Implants With Selenium and Hyaluronic Acid Coating for Dental Applications
Abstract
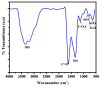
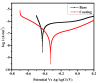
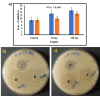
Background The current study demonstrated improved efficiency of commercially pure titanium (CP-Ti) dental implants with a biocompatible coating of selenium (Se) and hyaluronic acid (HA). Methods The sol-gel solution was made with hyaluronic acid and selenium nitrate in a 1:1 ratio. The coating sample was subjected to characterization studies such as Fourier Transform Infrared (FTIR) spectroscopy, surface morphology analysis, contact angle, etc., to confirm the coating. The antimicrobial activity of the coating was studied by analyzing the zone of inhibition. Results The FTIR spectroscopy was analyzed to confirm the functional groups of Se/HA. The surface morphology of the coated sample appeared as tiny needles with a plate-like surface. The potentiodynamic polarization studies revealed that the coated Ti samples exhibit superior corrosion resistance. The antimicrobial activity of Staphylococcus aureus was found to be more effective at a concentration of 100 mg. Furthermore, the basic criteria of biomaterials were analyzed for hemocompatibility studies, which suggested a non-hemolytic character. Conclusion The biocompatible coating of Se and HA has proven to be of superior corrosion resistance and antimicrobial activity resistance, which validate the usage of dental implants.
Keywords: antibacterial effect; hyaluronic acid; selenium; sol-gel coating; titanium.
Copyright © 2024, Ganesh et al.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors have declared that no competing interests exist.
Figures



Similar articles
-
In vitro corrosion behavior of bioceramic, metallic, and bioceramic-metallic coated stainless steel dental implants.Dent Mater. 2003 May;19(3):188-98. doi: 10.1016/s0109-5641(02)00029-5. Dent Mater. 2003. PMID: 12628430
-
Titanium coating: introducing an antibacterial and bioactive chitosan-alginate film on titanium by spin coating.Biomed Tech (Berl). 2020 Oct 25;65(5):621-630. doi: 10.1515/bmt-2018-0108. Biomed Tech (Berl). 2020. PMID: 32333647
-
Effect of titanium dioxide intermediate layer on scratch and corrosion resistance of sol-gel-derived HA coating applied on Ti-6Al-4V substrate.Prog Biomater. 2021 Dec;10(4):259-269. doi: 10.1007/s40204-021-00169-0. Epub 2021 Nov 6. Prog Biomater. 2021. PMID: 34741278 Free PMC article.
-
Enhanced corrosion resistance and cytocompatibility of biomimetic hyaluronic acid functionalised silane coating on AZ31 Mg alloy for orthopaedic applications.J Mater Sci Mater Med. 2018 Aug 28;29(9):144. doi: 10.1007/s10856-018-6150-5. J Mater Sci Mater Med. 2018. PMID: 30155669
-
Surface characterization and corrosion behavior of calcium phosphate-base composite layer on titanium and its alloys via plasma electrolytic oxidation: A review paper.Mater Sci Eng C Mater Biol Appl. 2015 Dec 1;57:397-413. doi: 10.1016/j.msec.2015.07.058. Epub 2015 Aug 5. Mater Sci Eng C Mater Biol Appl. 2015. PMID: 26354281 Review.
Cited by
-
Coating Polyetheretherketone Implant Surface With Titanium Oxide Nanoparticles and Hyaluronic Acid: An In Vitro Study.Cureus. 2025 Jan 13;17(1):e77383. doi: 10.7759/cureus.77383. eCollection 2025 Jan. Cureus. 2025. PMID: 39944440 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Silver nanoparticles incorporated polyaniline on TiO2 nanotube arrays: a nanocomposite platform to enhance the biocompatibility and antibiofilm. Perumal A, Kannan S, Nallaiyan R. Surf Interfaces. 2021;22
-
- Effect of hafnium coating on osseointegration of titanium implants: a split mouth animal study. Rajaraman V, Nallaswamy D, Ganapathy D, Rajeshkumar S, Ariga P, Ganesh K. J Nanomater. 2021
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous
