Immune reconstitution inflammatory syndrome-associated lymphoma: A retrospective Brazilian cohort
- PMID: 38406522
- PMCID: PMC10887249
- DOI: 10.1002/jha2.835
Immune reconstitution inflammatory syndrome-associated lymphoma: A retrospective Brazilian cohort
Abstract
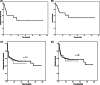
After initiating combined antiretroviral therapy (cART), individuals with human immunodeficiency virus (HIV) may develop Hodgkin/non-Hodgkin lymphoma due to immune reconstitution inflammatory syndrome (IRIS). This retrospective cohort study evaluated the incidence, clinical features and prognosis of IRIS-associated lymphomas in Brazilian patients. Incidence in 2000-2019 was 9.8% (27/276 patients with HIV and lymphoma; viral load drop >1 log). Time between HIV diagnosis and cART initiation was <1 year in 70.3% of cases. Time between cART initiation and lymphoma diagnosis was <3 months in 11 cases and 3-6 months in 16 cases. Overall and progression-free survival rates were similar between cases of non-IRIS-associated lymphoma and IRIS-associated lymphoma.
Keywords: antiretroviral therapy; immune reconstitution inflammatory syndrome; lymphoma.
© 2023 Centro Universitário São Camilo. eJHaem published by British Society for Haematology and John Wiley & Sons Ltd.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare they have no conflicts of interest.
Figures
References
-
- Brazilian Ministry of Health . Protocolo clínico e diretrizes terapêuticas para manejo da infecção pelo HIV em adultos [Clinical Protocol and therapeutic guidelines for the management of HIV infection in adults]. Brasília: Ministério da Saúde, Secretaria de Vigilância em Saúde; 2018.
-
- Meintjes G, Lawn SD, Scano F, Maartens G, French MA, Worodria W, et al. International Network for the Study of HIV‐associated IRIS. Tuberculosis‐associated immune reconstitution inflammatory syndrome: case definitions for use in resource‐limited settings. Lancet Infect Dis. 2008;8:516–523. - PMC - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
