Quantitative evaluation of embedding resins for volume electron microscopy
- PMID: 38406585
- PMCID: PMC10884229
- DOI: 10.3389/fnins.2024.1286991
Quantitative evaluation of embedding resins for volume electron microscopy
Abstract
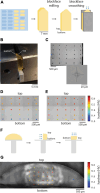
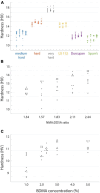
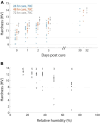
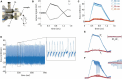
Optimal epoxy resin embedding is crucial for obtaining consistent serial sections from large tissue samples, especially for block faces spanning >1 mm2. We report a method to quantify non-uniformity in resin curing using block hardness measurements from block faces. We identify conditions that lead to non-uniform curing as well as a procedure to monitor the hardness of blocks for a wide range of common epoxy resins used for volume electron microscopy. We also assess cutting repeatability and uniformity by quantifying the transverse and sectional cutting forces during ultrathin sectioning using a sample-mounted force sensor. Our findings indicate that screening and optimizing resin formulations is required to achieve the best repeatability in terms of section thickness. Finally, we explore the encapsulation of irregularly shaped tissue samples in a gelatin matrix prior to epoxy resin embedding to yield more uniform sections.
Keywords: cutting forces; epoxy resin; hardness; tissue embedding; volume electron microscopy (vEM).
Copyright © 2024 Tegethoff and Briggman.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Quantitative STEM imaging of electron beam induced mass loss of epoxy resin sections.Ultramicroscopy. 2019 Jul;202:44-50. doi: 10.1016/j.ultramic.2019.03.018. Epub 2019 Mar 30. Ultramicroscopy. 2019. PMID: 30953993
-
Epoxy resins in electron microscopy.J Biophys Biochem Cytol. 1960 Feb;7(1):27-30. doi: 10.1083/jcb.7.1.27. J Biophys Biochem Cytol. 1960. PMID: 13822825 Free PMC article.
-
A determination of thickness and surface relief in reembedded sections of an epoxy- and a melamine-resin containing ferritin as size standard.Ultramicroscopy. 1985;17(2):141-6. doi: 10.1016/0304-3991(85)90007-5. Ultramicroscopy. 1985. PMID: 4071833
-
Artifacts caused by dehydration and epoxy embedding in transmission electron microscopy.Microsc Res Tech. 1993 Dec 15;26(6):496-512. doi: 10.1002/jemt.1070260604. Microsc Res Tech. 1993. PMID: 8305727 Review.
-
Antigen detection on resin sections and methods for improving the immunogold labeling by manipulating the resin.Histol Histopathol. 1998 Jan;13(1):275-81. doi: 10.14670/HH-13.275. Histol Histopathol. 1998. PMID: 9476657 Review.
Cited by
-
Eye features and retinal photoreceptors of the nocturnal aardvark (Orycteropus afer, Tubulidentata).PLoS One. 2025 Mar 24;20(3):e0314252. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0314252. eCollection 2025. PLoS One. 2025. PMID: 40127097 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Acetarin J.-D., Carlemalm E., Kellenberger E., Villiger W. (1987). Correlation of some mechanical properties of embedding resins with their behaviour in microtomy. J. Electron Microsc. Tech. 6 63–79. 10.1002/jemt.1060060109 - DOI
-
- Alexander S.-C., Michał J., Daniel R. B., Art P., Yuelong W., Tim B., et al. (2021). A connectomic study of a petascale fragment of human cerebral cortex. bioRxiv [Preprint] 10.1101/2021.05.29.446289 - DOI
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

