Stereotactic body radiotherapy of central lung tumours using a 1.5 T MR-linac: First clinical experiences
- PMID: 38406645
- PMCID: PMC10885732
- DOI: 10.1016/j.ctro.2024.100744
Stereotactic body radiotherapy of central lung tumours using a 1.5 T MR-linac: First clinical experiences
Abstract
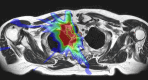
Background: MRI-guidance may aid better discrimination between Organs at Risk (OARs) and target volumes in proximity of the mediastinum. We report the first clinical experiences with Stereotactic Body Radiotherapy (SBRT) of (ultra)central lung tumours on a 1.5 T MR-linac.
Materials and methods: Patients with an (ultra)central lung tumour were selected for MR-linac based SBRT treatment. A T2-weighted 3D sequence MRI acquired during free breathing was used for daily plan adaption. Prior to each fraction, contours of Internal Target Volume (ITV) and OARs were deformably propagated and amended by a radiation oncologist. Inter-fractional changes in volumes and coverage of target volumes as well as doses in OARs were evaluated in offline and online treatment plans.
Results: Ten patients were treated and completed 60 Gy in 8 or 12 fractions. In total 104 fractions were delivered. The median time in the treatment room was 41 min with a median beam-on time of 8.9 min. No grade ≥3 acute toxicity was observed. In two patients, the ITV significantly decreased during treatment (58 % and 37 %, respectively) due to tumour shrinkage. In the other patients, 81 % of online ITVs were within ±15 % of the volume of fraction 1. Comparison with the pre-treatment plan showed that ITV coverage of the online plan was similar in 52 % and improved in 34 % of cases. Adaptation to meet OAR constraints, led to decreased ITV coverage in 14 %.
Conclusions: We describe the workflow for MR-guided Radiotherapy and the feasibility of using 1.5 T MR-linac for SBRT of (ultra) central lung tumours.
Keywords: (Ultra) central lung tumour; MR-Linac; SBRT.
© 2024 The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no known competing financial interests or personal relationships that could have appeared to influence the work reported in this paper.
Figures

Similar articles
-
MR-guided adaptive versus ITV-based stereotactic body radiotherapy for hepatic metastases (MAESTRO): a randomized controlled phase II trial.Radiat Oncol. 2022 Mar 27;17(1):59. doi: 10.1186/s13014-022-02033-2. Radiat Oncol. 2022. PMID: 35346270 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial.
-
Feasibility of Adaptive MR-guided Stereotactic Body Radiotherapy (SBRT) of Lung Tumors.Cureus. 2018 Apr 4;10(4):e2423. doi: 10.7759/cureus.2423. Cureus. 2018. PMID: 29872603 Free PMC article.
-
The impact of margin reduction on radiation dose distribution of ultra-hypofractionated prostate radiotherapy utilizing a 1.5-T MR-Linac.J Appl Clin Med Phys. 2024 Jan;25(1):e14179. doi: 10.1002/acm2.14179. Epub 2023 Nov 27. J Appl Clin Med Phys. 2024. PMID: 38013636 Free PMC article.
-
On the feasibility of cardiac substructure sparing in magnetic resonance imaging guided stereotactic lung radiotherapy.Med Phys. 2023 Jan;50(1):397-409. doi: 10.1002/mp.16028. Epub 2022 Oct 24. Med Phys. 2023. PMID: 36210631 Free PMC article.
-
Harnessing the Power of Radiotherapy for Lung Cancer: A Narrative Review of the Evolving Role of Magnetic Resonance Imaging Guidance.Cancers (Basel). 2024 Jul 30;16(15):2710. doi: 10.3390/cancers16152710. Cancers (Basel). 2024. PMID: 39123438 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Recent technical advancements and clinical applications of MR-guided radiotherapy in lung cancer treatment.Front Oncol. 2025 Jul 1;15:1622060. doi: 10.3389/fonc.2025.1622060. eCollection 2025. Front Oncol. 2025. PMID: 40666105 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Organs at risk proximity in central lung stereotactic ablative radiotherapy: A comparison of four-dimensional computed tomography and magnetic resonance-guided breath-hold delivery techniques.Phys Imaging Radiat Oncol. 2025 Apr 2;34:100761. doi: 10.1016/j.phro.2025.100761. eCollection 2025 Apr. Phys Imaging Radiat Oncol. 2025. PMID: 40242808 Free PMC article.
-
Real-time tracking of lung tumors using a 1.5T Elekta Unity MR-Linac: first clinical experiences.Front Oncol. 2025 Apr 8;15:1569428. doi: 10.3389/fonc.2025.1569428. eCollection 2025. Front Oncol. 2025. PMID: 40313246 Free PMC article.
-
MR-guided online adaptive stereotactic body radiotherapy (MRgSBRT) of primary lung tumors and lung oligometastases.Strahlenther Onkol. 2025 Jun;201(6):637-644. doi: 10.1007/s00066-024-02328-1. Epub 2024 Dec 2. Strahlenther Onkol. 2025. PMID: 39622976
-
Investigation of intrafractional spinal cord and spinal canal movement during stereotactic MR-guided online adaptive radiotherapy for kidney cancer.PLoS One. 2024 Oct 30;19(10):e0312032. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0312032. eCollection 2024. PLoS One. 2024. PMID: 39475854 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Yan M., Louie A.V., Kotecha R., Ashfaq Ahmed M., Zhang Z., Guckenberger M., et al. Stereotactic body radiotherapy for Ultra-Central lung Tumors: A systematic review and Meta-Analysis and International Stereotactic Radiosurgery Society practice guidelines. Lung Cancer. 2023;182 doi: 10.1016/j.lungcan.2023.107281. - DOI - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

