Regorafenib modulation of the angiopoietin/TIE2 axis in a mouse model of sepsis-induced lung injury
- PMID: 38406775
- PMCID: PMC10893570
- DOI: 10.25122/jml-2023-0135
Regorafenib modulation of the angiopoietin/TIE2 axis in a mouse model of sepsis-induced lung injury
Abstract
Sepsis, often resulting from an immune response overreaction to microorganisms and their products, can lead to acute lung injury through inflammation mediated by excessive cytokines. This study aimed to investigate the effects of regorafenib on lung injury in mice following the induction of sepsis. We divided mice into four groups (n=6 each): a sham group (undergoing laparotomy without cecal ligation and puncture [CLP]), a CLP group, a vehicle group, and a regorafenib-treated group (30 mg/kg IP, administered one hour before CLP). TNF-α, IL-1β, VEGF, MPO, caspase-11, and Ang-2 levels were significantly increased (p<0.05) in the CLP group compared to the sham group, while the regorafenib group showed significant reductions in these markers versus the CLP group (p< 0.05). In contrast, Ang-1 levels, which were reduced in the CLP group (p<0.05) compared to the sham group, were elevated in the regorafenib group compared to the CLP group. Quantitative real-time PCR revealed a significant decrease in TIE2 and VE-cadherin mRNA expression in the lung tissue of the CLP group compared to the sham group. There were no significant differences in mRNA expression of the TIE2 gene between the regorafenib and CLP group. However, VE-cadherin significantly increased after regorafenib treatment. Regorafenib demonstrated lung-protective effects through its anti-inflammatory and antiangiogenic activities and its influence on lung tissue mRNA expression of the cadherin gene.
Keywords: Ang/TIE2 axis; Ang: Angiopoietin; CLP; CLP: Cecal Ligation and Puncture; HKG: Housekeeping Gene; IL-1β: Interleukin-1 beta; MPO: Myeloperoxidase; NF-κB: Nuclear Factor kappa-light-chain-enhancer of activated B cells; TIE2: Tyrosine Kinase with Immunoglobulin-like and EGF-like Domains 2; TNF-α: Tumor Necrosis Factor-alpha; VEGF; VEGF: Vascular Endothelial Growth Factor; cadherin; qPCR: Quantitative Real-Time PCR; regorafenib; sepsis.
© 2023 The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
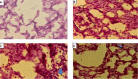
Figures






References
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous
