Azacitidine induced lung injury: report and contemporary discussion on diagnosis and management
- PMID: 38406809
- PMCID: PMC10884222
- DOI: 10.3389/fonc.2024.1345492
Azacitidine induced lung injury: report and contemporary discussion on diagnosis and management
Abstract
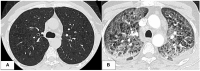
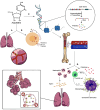
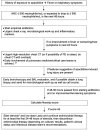
Azacitidine, a hypomethylating agent, has caused a paradigm shift in the outcomes of patients with myelodysplastic syndrome (MDS) and acute myeloid leukemia (AML) who are not eligible for stem cell transplantation, particularly in combination with BCL2 and IDH inhibitors. Azacitidine and Azacitidine-based combinations have been widely considered a safe low-intensity therapy when compared to traditional conventional treatments. The development of lung toxicity from azacitidine is not a well-characterized adverse event. However, if it happens, it can be fatal, especially if not recognized and treated promptly. In this review, we aim to familiarize the reader with the presentation of azacitidine-induced lung injury, provide our suggested approach to management based on our experience and the current understanding of its mechanism, and review the literature of 20 case reports available on this topic.
Keywords: acute lung injury; acute myeloid leukemia; azaciditine; azacitidine induced lung injury myelodysplastic syndrome; hypomethylating agents; pneumonitis.
Copyright © 2024 Alyamany, Alnughmush, Almutlaq, Alyamany and Alfayez.
Conflict of interest statement
Author MA was employed by Honoraria: Johnson & Johnson, Pfizer, Astellas, Novartis, Amgen, AstraZeneca, AbbVie, Advisory board: Johnson & Johnson, Biologix, Eli Lilly. Research support: Abbvie, AstraZeneca. The remaining authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
One plus one does not always equal two, especially with regard to hypomethylating agents: the question of synergy of azacitidine and lenalidomide for treatment of relapsed acute myeloid leukemia and myelodysplastic syndromes post allogeneic hematopoietic stem cell transplant.Expert Rev Hematol. 2019 Aug;12(8):575-578. doi: 10.1080/17474086.2019.1635005. Epub 2019 Jun 26. Expert Rev Hematol. 2019. PMID: 31225770
-
Feasibility of allogeneic stem-cell transplantation after azacitidine bridge in higher-risk myelodysplastic syndromes and low blast count acute myeloid leukemia: results of the BMT-AZA prospective study.Ann Oncol. 2017 Jul 1;28(7):1547-1553. doi: 10.1093/annonc/mdx154. Ann Oncol. 2017. PMID: 28368509 Clinical Trial.
-
Clinical status of induction therapy incorporating a hypomethylating agent for newly diagnosed adult acute myeloid leukemia compared to the standard 7+3 regimen.Expert Rev Hematol. 2023 Jul-Dec;16(10):761-771. doi: 10.1080/17474086.2023.2256472. Epub 2023 Sep 8. Expert Rev Hematol. 2023. PMID: 37670667 Review.
-
Azacitidine-Induced Interstitial Pneumonitis.Am J Ther. 2016 Sep-Oct;23(5):e1205-8. doi: 10.1097/MJT.0000000000000300. Am J Ther. 2016. PMID: 26371947
-
Oral Azacitidine (CC-486) for the Treatment of Myelodysplastic Syndromes and Acute Myeloid Leukemia.Oncologist. 2015 Dec;20(12):1404-12. doi: 10.1634/theoncologist.2015-0165. Epub 2015 Oct 13. Oncologist. 2015. PMID: 26463870 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
DNA methylation modification in Idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis.Front Cell Dev Biol. 2024 Jun 10;12:1416325. doi: 10.3389/fcell.2024.1416325. eCollection 2024. Front Cell Dev Biol. 2024. PMID: 38915445 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Lack of Content Uniformity in Azacitidine Vials.Contact Context. 2024;2024:10.6084/m9.figshare.26828245. doi: 10.6084/m9.figshare.26828245. Epub 2024 Aug 27. Contact Context. 2024. PMID: 40454370 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Ahrari A, Sabloff M, Bredeson C, Pakhale S, Souza C, Zwicker J, et al. . Rare respiratory and neurologic adverse reactions to azacitidine in the treatment of myelodysplastic syndrome of patients treated at the ottawa hospital. J Hematol (2015) 4(4):231–4. doi: 10.14740/jh227w - DOI
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

