Estimates of Incidence and Predictors of Fatiguing Illness after SARS-CoV-2 Infection
- PMID: 38407166
- PMCID: PMC10902536
- DOI: 10.3201/eid3003.231194
Estimates of Incidence and Predictors of Fatiguing Illness after SARS-CoV-2 Infection
Abstract
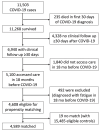
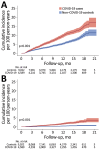
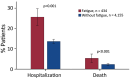
This study aimed to estimate the incidence rates of post-COVID-19 fatigue and chronic fatigue and to quantify the additional incident fatigue caused by COVID-19. We analyzed electronic health records data of 4,589 patients with confirmed COVID-19 during February 2020-February 2021 who were followed for a median of 11.4 (interquartile range 7.8-15.5) months and compared them to data from 9,022 propensity score-matched non-COVID-19 controls. Among COVID-19 patients (15% hospitalized for acute COVID-19), the incidence rate of fatigue was 10.2/100 person-years and the rate of chronic fatigue was 1.8/100 person-years. Compared with non-COVID-19 controls, the hazard ratios were 1.68 (95% CI 1.48-1.92) for fatigue and 4.32 (95% CI 2.90-6.43) for chronic fatigue. The observed association between COVID-19 and the significant increase in the incidence of fatigue and chronic fatigue reinforces the need for public health actions to prevent SARS-CoV-2 infections.
Keywords: COVID-19; ME/CFS; PASC; PCC; SARS-CoV-2; coronavirus disease 2019; fatigue; incidence; myalgic encephalomyelitis/chronic fatigue syndrome; post COVID-19 conditions; post-acute sequelae of SARS-CoV-2 infection; respiratory infections; severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2; viruses; zoonoses.
Figures
References
-
- Centers for Disease Control and Prevention. Long COVID—household pulse survey [cited 2023 Feb 6]. https://www.cdc.gov/nchs/covid19/pulse/long-covid.htm
-
- O’Mahoney LL, Routen A, Gillies C, Ekezie W, Welford A, Zhang A, et al. The prevalence and long-term health effects of Long Covid among hospitalised and non-hospitalised populations: A systematic review and meta-analysis. EClinicalMedicine. 2022;55:101762. 10.1016/j.eclinm.2022.101762 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

