Helicobacter pylori upregulates circPGD and promotes development of gastric cancer
- PMID: 38407616
- PMCID: PMC10896836
- DOI: 10.1007/s00432-023-05537-w
Helicobacter pylori upregulates circPGD and promotes development of gastric cancer
Abstract
Purpose: Helicobacter pylori (H. pylori) has unique biochemical traits and pathogenic mechanisms, which make it a substantial cause of gastrointestinal cancers. Circular RNAs (circRNAs) have concurrently been identified as an important participating factor in the pathophysiology of several different cancers. However, the underlying processes and putative interactions between H. pylori and circRNAs have received very little attention. To address this issue, we explored the interaction between H. pylori and circRNAs to investigate how they might jointly contribute to the occurrence and development of gastric cancer.
Methods: Changes in circPGD expression in H. pylori were detected using qRT-PCR. Cell proliferation and migration changes were assayed by colony formation, the CCK-8 assay and the transwell assay. Apoptosis was measured by flow cytometry. Western blot was conducted to detect changes in cell migration, apoptosis, proliferation and inflammation-associated proteins. QRT-PCR was used to measure changes in circPGD and inflammation-associated factors.
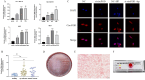
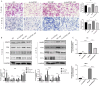
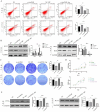
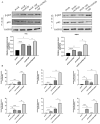
Results: We found that H. pylori induced increased circPGD expression in infected human cells and facilitated gastric cancer progression in three ways by promoting cell proliferation and migration, enhancing the inflammatory response, and inhibiting apoptosis.
Conclusions: CircPGD appears to play a role in H. pylori-related gastric cancer and may thus be a viable, novel target for therapeutic intervention.
Keywords: Apoptosis; Gastric cancer; Helicobacter pylori; Inflammation; circRNAs.
© 2024. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures



References
-
- Domínguez-Martínez DA, Fontes-Lemus JI, García-Regalado A, Juárez-Flores Á, Fuentes-Pananá EM (2023) IL-8 secreted by gastric epithelial cells infected with Helicobacter pylori CagA positive strains is a chemoattractant for Epstein–Barr virus infected B lymphocytes. Viruses 15(3):651. 10.3390/v15030651 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
- Grant No. 81772157/National Natural Science Foundation of China
- Grant No. 81772157/National Natural Science Foundation of China
- Grant No. 81772157/National Natural Science Foundation of China
- Grant No. 81772157/National Natural Science Foundation of China
- Grant No. 81772157/National Natural Science Foundation of China
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

