Cortical-sparing chronic traumatic encephalopathy (CSCTE): a distinct subtype of CTE
- PMID: 38407651
- PMCID: PMC11348287
- DOI: 10.1007/s00401-024-02690-5
Cortical-sparing chronic traumatic encephalopathy (CSCTE): a distinct subtype of CTE
Abstract
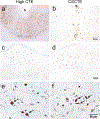
Chronic traumatic encephalopathy (CTE) is a neurodegenerative disease caused by repetitive head impacts (RHI) and pathologically defined as neuronal phosphorylated tau aggregates around small blood vessels and concentrated at sulcal depths. Cross-sectional studies suggest that tau inclusions follow a stereotyped pattern that begins in the neocortex in low stage disease, followed by involvement of the medial temporal lobe and subcortical regions with significant neocortical burden in high stage CTE. Here, we define a subset of brain donors with high stage CTE and with a low overall cortical burden of tau inclusions (mean semiquantitative value ≤1) and classify them as cortical-sparing CTE (CSCTE). Of 620 brain donors with pathologically diagnosed CTE, 66 (11%) met criteria for CSCTE. Compared to typical high stage CTE, those with CSCTE had a similar age at death and years of contact sports participation and were less likely to carry apolipoprotein ε4 (p < 0.05). CSCTE had less overall tau pathology severity, but a proportional increase of disease burden in medial temporal lobe and brainstem regions compared to the neocortex (p's < 0.001). CSCTE also had lower prevalence of comorbid neurodegenerative disease. Clinically, CSCTE participants were less likely to have dementia (p = 0.023) and had less severe cognitive difficulties (as reported by informants using the Functional Activities Questionnaire (FAQ); p < 0.001, meta-cognitional index T score; p = 0.002 and Cognitive Difficulties Scale (CDS); p < 0.001,) but had an earlier onset age of behavioral (p = 0.006) and Parkinsonian motor (p = 0.013) symptoms when compared to typical high stage CTE. Other comorbid tauopathies likely contributed in part to these differences: when cases with concurrent Alzheimer dementia or frontal temporal lobar degeneration with tau pathology were excluded, differences were largely retained, but only remained significant for FAQ (p = 0.042), meta-cognition index T score (p = 0.014) and age of Parkinsonian motor symptom onset (p = 0.046). Overall, CSCTE appears to be a distinct subtype of high stage CTE with relatively greater involvement of subcortical and brainstem regions and less severe cognitive symptoms.
Keywords: Chronic traumatic encephalopathy; Neurodegenerative disease; Repetitive head impacts; Traumatic brain injury.
© 2024. This is a U.S. Government work and not under copyright protection in the US; foreign copyright protection may apply.
Figures
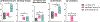
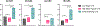
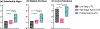
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
- RF1 NS132290/NS/NINDS NIH HHS/United States
- RF1 NS122854/NS/NINDS NIH HHS/United States
- U01NS086659/NS/NINDS NIH HHS/United States
- U54NS115266/NS/NINDS NIH HHS/United States
- RF1NS122854/NS/NINDS NIH HHS/United States
- U54 NS115266/NS/NINDS NIH HHS/United States
- K23NS102399/NS/NINDS NIH HHS/United States
- RF1 AG062348/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- NIRG-305779/ALZ/Alzheimer's Association/United States
- R01 NS122854/NS/NINDS NIH HHS/United States
- R01 AG075876/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- U01 NS086659/NS/NINDS NIH HHS/United States
- I01 BX002466/BX/BLRD VA/United States
- P30 AG072978/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- I01 BX005161/BX/BLRD VA/United States
- K23 NS102399/NS/NINDS NIH HHS/United States
- I01 BX005933/BX/BLRD VA/United States
- NIRG-362697/ALZ/Alzheimer's Association/United States
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

