TRENDS IN CHOLESTEROL AND LIPOPROTEINS ARE ASSOCIATED WITH ACUTE RESPIRATORY DISTRESS SYNDROME INCIDENCE AND DEATH AMONG SEPSIS PATIENTS
- PMID: 38407817
- PMCID: PMC10957110
- DOI: 10.1097/SHK.0000000000002295
TRENDS IN CHOLESTEROL AND LIPOPROTEINS ARE ASSOCIATED WITH ACUTE RESPIRATORY DISTRESS SYNDROME INCIDENCE AND DEATH AMONG SEPSIS PATIENTS
Abstract
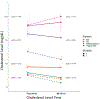
Objective: Compare changes in cholesterol and lipoprotein levels occurring in septic patients with and without acute respiratory distress syndrome (ARDS) and by survivorship. Methods: We reanalyzed data from prospective sepsis studies. Cholesterol and lipoprotein levels were analyzed using univariate testing to detect changes between septic patients with or without ARDS, and among ARDS survivors compared with nonsurvivors at enrollment (first 24 h of sepsis) and 48 to 72 h later. Results: 214 patients with sepsis were included of whom 48 had ARDS and 166 did not have ARDS. Cholesterol and lipoproteins among septic ARDS versus non-ARDS showed similar enrollment levels. However, 48 to 72 h after enrollment, change in median total cholesterol (48/72 h - enrollment) was significantly different between septic ARDS (-4, interquartile range [IQR] -23.5, 6.5, n = 35) and non-ARDS (0, -10.0, 17.5, P = 0.04; n = 106). When compared by ARDS survivorship, ARDS nonsurvivors (n = 14) had lower median total cholesterol levels (75.5, IQR 68.4, 93.5) compared with ARDS survivors (113.0, IQR 84.0, 126.8, P = 0.022), and lower median enrollment low-density lipoprotein cholesterol (LDL-C) levels (27, IQR 19.5-34.5) compared with ARDS survivors (43, IQR 27-67, P = 0.013; n = 33). Apolipoprotein A-I levels were also significantly lower in ARDS nonsurvivors (n = 14) (87.6, IQR 76.45-103.64) compared with ARDS survivors (130.0, IQR 73.25-165.47, P = 0.047; n = 33). At 48 to 72 h, for ARDS nonsurvivors, median levels of low-density lipoprotein cholesterol (9.0, IQR 4.3, 18.0; n = 10), LDL-C (17.0, IQR 5.0, 29.0; n = 9), and total cholesterol (59.0, 45.3, 81.5; n = 10) were significantly lower compared with ARDS survivors' (n = 25) levels of low-density lipoprotein cholesterol (20.0, IQR 12.0-39.0, P = 0.014), LDL-C (42.0, IQR 27.0-58.0, P = 0.019), and total cholesterol (105.0, IQR 91.0, 115.0, P = 0.003). Conclusions: Change in total cholesterol was different in septic ARDS versus non-ARDS. Total cholesterol, LDL-C, and apolipoprotein A-I levels were lower in ARDS nonsurvivors compared with survivors. Future studies of dysregulated cholesterol metabolism in septic ARDS patients are needed to understand biology and links to potential therapies.
Trial registration: ClinicalTrials.gov NCT02934997.
Copyright © 2023 by the Shock Society.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors report no conflict of interests.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Prescription of Controlled Substances: Benefits and Risks.2025 Jul 6. In: StatPearls [Internet]. Treasure Island (FL): StatPearls Publishing; 2025 Jan–. 2025 Jul 6. In: StatPearls [Internet]. Treasure Island (FL): StatPearls Publishing; 2025 Jan–. PMID: 30726003 Free Books & Documents.
-
IDENTIFYING A SEPSIS SUBPHENOTYPE CHARACTERIZED BY DYSREGULATED LIPOPROTEIN METABOLISM USING A SIMPLIFIED CLINICAL DATA ALGORITHM.Shock. 2025 Aug 1;64(2):218-225. doi: 10.1097/SHK.0000000000002605. Epub 2025 Apr 23. Shock. 2025. PMID: 40267485 Free PMC article.
-
Positioning for acute respiratory distress in hospitalised infants and children.Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2022 Jun 6;6(6):CD003645. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD003645.pub4. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2022. PMID: 35661343 Free PMC article.
-
Cardiovascular outcomes in patients with homozygous familial hypercholesterolaemia on lipoprotein apheresis initiated during childhood: long-term follow-up of an international cohort from two registries.Lancet Child Adolesc Health. 2024 Jul;8(7):491-499. doi: 10.1016/S2352-4642(24)00073-7. Epub 2024 May 14. Lancet Child Adolesc Health. 2024. PMID: 38759658 Free PMC article.
-
Low-carbohydrate versus balanced-carbohydrate diets for reducing weight and cardiovascular risk.Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2022 Jan 28;1(1):CD013334. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD013334.pub2. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2022. PMID: 35088407 Free PMC article.
Cited by
-
Hepatic Nuclear Factor Erythroid 2 Related Factor 1 Activity Promotes Host Defense in Endotoxemia and Bacterial Sepsis.Cell Mol Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2025;19(9):101550. doi: 10.1016/j.jcmgh.2025.101550. Epub 2025 May 29. Cell Mol Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2025. PMID: 40449845 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Diamond M, Peniston HL, Sanghavi D, Mahapatra S. Acute Respiratory Distress Syndrome. In: StatPearls. StatPearls Publishing; 2022. Accessed November 20, 2022. http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK436002/ - PubMed

