Meta-analysis of the effectiveness and safety of robotic-assisted versus laparoscopic transabdominal preperitoneal repair for inguinal hernia
- PMID: 38408054
- PMCID: PMC10896538
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0298989
Meta-analysis of the effectiveness and safety of robotic-assisted versus laparoscopic transabdominal preperitoneal repair for inguinal hernia
Abstract
Background: Inguinal hernia is a common global disease. This study aims to investigate the effectiveness and safety of robot-assisted transabdominal preperitoneal repair (RTAPP) and laparoscopic transabdominal preperitoneal repair (LTAPP) for inguinal hernia.
Methods: We conducted a thorough search in Cochrane Library, Embase, and PubMed for relevant clinical studies. After applying inclusion and exclusion criteria, the quality of selected studies was assessed using the Jadad scale for randomized controlled studies and the Newcastle-Ottawa scale for observational studies. Meta-analysis was performed using RevMan 5.3 software.
Results: A total of ten studies were included, comprising two randomized controlled studies and eight non-randomized controlled studies. Meta-analysis results revealed no statistically significant differences between the RTAPP group and the LTAPP group regarding hospital stay [MD = 0.21 days, 95% CI (-0.09, 0.51), P = 0.17], incidence of seroma [OR = 0.85, 95% CI(0.45, 1.59), P = 0.61], overall complication rate [OR = 1.22, 95% CI(0.68, 2.18), P = 0.51], readmission rate [OR = 1.31, 95% CI(0.23, 7.47), P = 0.76], and recurrence rate [OR = 0.82, 95% CI(0.22, 3.07), P = 0.77]. However, the RTAPP group had longer operation time compared to the LTAPP group [MD = 14.02 minutes, 95% CI (6.65, 21.39), P = 0.0002], and the cost of the RTAPP procedure was higher than that of the LTAPP procedure [MD = $4.17 thousand, 95% CI (2.59, 5.76), P<0.00001].
Conclusion: RTAPP for inguinal hernia is a safe and feasible approach, however, it is associated with increased operation time and treatment costs.
Copyright: © 2024 Li et al. This is an open access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License, which permits unrestricted use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided the original author and source are credited.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors have declared that no competing interests exist.
Figures

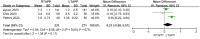
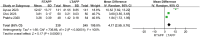


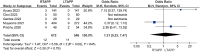
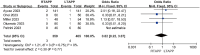
Similar articles
-
Robotic versus laparoscopic transabdominal preperitoneal (TAPP) approaches to bilateral hernia repair: a multicenter retrospective study using propensity score matching analysis.Surg Endosc. 2023 Feb;37(2):1188-1193. doi: 10.1007/s00464-022-09614-y. Epub 2022 Sep 26. Surg Endosc. 2023. PMID: 36156737 Free PMC article.
-
Introduction and Short-Term Outcomes of Robot-Assisted Transabdominal Preperitoneal Inguinal Hernia Repair at a Municipal Hospital by a Robotic Surgery Novice: A Single-Center, Observational Study.Asian J Endosc Surg. 2025 Jan-Dec;18(1):e13421. doi: 10.1111/ases.13421. Asian J Endosc Surg. 2025. PMID: 39689876
-
Short-term outcomes and inflammatory stress response following laparoscopy or robotic-assisted transabdominal preperitoneal inguinal hernia repair (TAPP): study protocol for a prospective, randomized trial (ROLAIS).Trials. 2024 Aug 8;25(1):529. doi: 10.1186/s13063-024-08361-w. Trials. 2024. PMID: 39118135 Free PMC article.
-
Navigating hernia sac management in minimally invasive inguinal hernia repair: to abandon or to reduce? An updated systematic review and meta-analysis.Surg Endosc. 2024 Dec;38(12):7045-7054. doi: 10.1007/s00464-024-11323-7. Epub 2024 Oct 23. Surg Endosc. 2024. PMID: 39441355
-
Is the transection of the hernia sac during laparoscopic inguinal hernioplasty safe and feasible? An updated systematic review and meta-analysis.Updates Surg. 2024 Dec;76(8):2733-2743. doi: 10.1007/s13304-024-02025-9. Epub 2024 Oct 24. Updates Surg. 2024. PMID: 39446302
Cited by
-
Shorter operative times following robotic-assisted transabdominal preperitoneal inguinal hernia repair (TAPP) compared to laparoscopic TAPP: the Danish Inguinal Randomized Controlled Trial (DIRECT).Hernia. 2025 Jul 9;29(1):227. doi: 10.1007/s10029-025-03402-y. Hernia. 2025. PMID: 40632168 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial.
-
Single-port versus multi-port laparoscopic and robotic inguinal hernia repair: a systematic review and network meta-analysis.Surg Endosc. 2025 Jan;39(1):530-544. doi: 10.1007/s00464-024-11321-9. Epub 2024 Oct 17. Surg Endosc. 2025. PMID: 39419843
-
Modern Perspectives on Inguinal Hernia Repair: A Narrative Review on Surgical Techniques, Mesh Selection and Fixation Strategies.J Clin Med. 2025 Jul 9;14(14):4875. doi: 10.3390/jcm14144875. J Clin Med. 2025. PMID: 40725568 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Clinical and Patient-Reported Outcomes of Robotic Versus Laparoscopic Inguinal Hernia Repair.JSLS. 2025 Apr-Jun;29(2):e2025.00005. doi: 10.4293/JSLS.2025.00005. Epub 2025 May 7. JSLS. 2025. PMID: 40336806 Free PMC article.
-
Groin hernia.Nat Rev Dis Primers. 2025 Jul 3;11(1):47. doi: 10.1038/s41572-025-00631-4. Nat Rev Dis Primers. 2025. PMID: 40610521 Review.
References
-
- Jensen KK, Henriksen NA, Jorgensen LN. Inguinal hernia epidemiology. Textbook of hernia. 2017: 23–27.
-
- Wang G, Zeng Y, Sheng X. Personnel Management in the Robotic Surgery Room. Robotic Surgery and Nursing. 2021: 111–115.
-
- Comparetto C, Borruto F. Applications of Robotics in Gynecological Surgery//Design and Control Advances in Robotics. IGI Global. 2023: 256–294.
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

