Extracellular vesicle formation in Euryarchaeota is driven by a small GTPase
- PMID: 38408251
- PMCID: PMC10927574
- DOI: 10.1073/pnas.2311321121
Extracellular vesicle formation in Euryarchaeota is driven by a small GTPase
Abstract
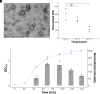
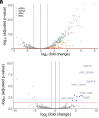
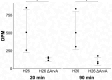
Since their discovery, extracellular vesicles (EVs) have changed our view on how organisms interact with their extracellular world. EVs are able to traffic a diverse array of molecules across different species and even domains, facilitating numerous functions. In this study, we investigate EV production in Euryarchaeota, using the model organism Haloferax volcanii. We uncover that EVs enclose RNA, with specific transcripts preferentially enriched, including those with regulatory potential, and conclude that EVs can act as an RNA communication system between haloarchaea. We demonstrate the key role of an EV-associated small GTPase for EV formation in H. volcanii that is also present across other diverse evolutionary branches of Archaea. We propose the name, ArvA, for the identified family of archaeal vesiculating GTPases. Additionally, we show that two genes in the same operon with arvA (arvB and arvC) are also involved in EV formation. Both, arvB and arvC, are closely associated with arvA in the majority of other archaea encoding ArvA. Our work demonstrates that small GTPases involved in membrane deformation and vesiculation, ubiquitous in Eukaryotes, are also present in Archaea and are widely distributed across diverse archaeal phyla.
Keywords: Archaea; Haloferax volcanii; extracellular vesicles; small GTPase; small RNAs.
Conflict of interest statement
Competing interests statement:The authors declare no competing interest.
Figures
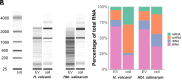


Similar articles
-
Transcriptional Landscape and Regulatory Roles of Small Noncoding RNAs in the Oxidative Stress Response of the Haloarchaeon Haloferax volcanii.J Bacteriol. 2018 Apr 9;200(9):e00779-17. doi: 10.1128/JB.00779-17. Print 2018 May 1. J Bacteriol. 2018. PMID: 29463600 Free PMC article.
-
RNA polyadenylation and degradation in different Archaea; roles of the exosome and RNase R.Nucleic Acids Res. 2006;34(20):5923-31. doi: 10.1093/nar/gkl763. Epub 2006 Oct 25. Nucleic Acids Res. 2006. PMID: 17065466 Free PMC article.
-
CdrS Is a Global Transcriptional Regulator Influencing Cell Division in Haloferax volcanii.mBio. 2021 Aug 31;12(4):e0141621. doi: 10.1128/mBio.01416-21. Epub 2021 Jul 13. mBio. 2021. PMID: 34253062 Free PMC article.
-
Haloferax volcanii-a model archaeon for studying DNA replication and repair.Open Biol. 2020 Dec;10(12):200293. doi: 10.1098/rsob.200293. Epub 2020 Dec 2. Open Biol. 2020. PMID: 33259746 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Small regulatory RNAs in Archaea.RNA Biol. 2014;11(5):484-93. doi: 10.4161/rna.28452. Epub 2014 Mar 31. RNA Biol. 2014. PMID: 24755959 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Global Distribution and Diversity of Haloarchaeal pL6-Family Plasmids.Genes (Basel). 2024 Aug 26;15(9):1123. doi: 10.3390/genes15091123. Genes (Basel). 2024. PMID: 39336713 Free PMC article.
-
RNA communication between organisms inspires innovative eco-friendly strategies for disease control.Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol. 2025 Feb;26(2):81-82. doi: 10.1038/s41580-024-00807-y. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol. 2025. PMID: 39548286 No abstract available.
-
The Asgard archaeal origins of Arf family GTPases involved in eukaryotic organelle dynamics.Nat Microbiol. 2025 Feb;10(2):495-508. doi: 10.1038/s41564-024-01904-6. Epub 2025 Jan 23. Nat Microbiol. 2025. PMID: 39849086
-
Cell division protein CdpA organises and anchors the midcell ring in haloarchaea.Nat Commun. 2025 May 31;16(1):5076. doi: 10.1038/s41467-025-60079-8. Nat Commun. 2025. PMID: 40450033 Free PMC article.
-
Extracellular Vesicles in Bacteria, Archaea, and Eukaryotes: Mechanisms of Inter-Kingdom Communication and Clinical Implications.Microorganisms. 2025 Mar 11;13(3):636. doi: 10.3390/microorganisms13030636. Microorganisms. 2025. PMID: 40142528 Free PMC article. Review.
References
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

