Family Caregivers' Management of Behavioral Expressions of Dementia
- PMID: 38408276
- PMCID: PMC11127109
- DOI: 10.1093/geront/gnae020
Family Caregivers' Management of Behavioral Expressions of Dementia
Abstract
Background and objectives: Behavioral expressions of dementia are often stressful for family caregivers to manage as they strive to ensure their relative's needs are met. Guided by Lazarus and Folkman's Transactional Model of Stress and Coping, we identified specific behaviors that disrupt daily routines and challenge the achievement of caregiving goals, and the approaches and strategies caregivers employ to address them.
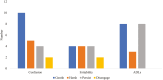
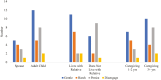
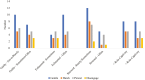
Research design and methods: We conducted semistructured interviews with 30 family caregivers in rural Appalachia caring for a relative living with dementia. Analysis involved use of open and focused coding processes to identify the ways caregivers managed behaviors and bar graphs to examine management approaches relative to categories of behaviors and caregiver demographic and emotional well-being variables.
Results: Analyses revealed 10 types of behavioral expressions of dementia associated with confusion, irritability, and resistance to engaging in necessary activities of daily living. Caregiver approaches to managing behaviors included gentle persuasion, being harsh by yelling or threatening, being persistent in expecting the person with dementia to complete the tasks at hand, disengaging by postponing the activity, and employing a combination of strategies. Approaches differed across types of behavior and caregiver demographics and had varying effects on caregiver well-being.
Discussion and implications: Uncovering specific behaviors family caregivers of persons living with dementia found bothersome, caregivers' adaptive strategies for managing behaviors, and the impact of those approaches provides new information to inform training on effective dementia caregiving practices and development of targeted intervention programs for dementia care.
Keywords: Caregiver well-being; Coping strategies; Dementia care; Rural.
© The Author(s) 2024. Published by Oxford University Press on behalf of The Gerontological Society of America. All rights reserved. For commercial re-use, please contact reprints@oup.com for reprints and translation rights for reprints. All other permissions can be obtained through our RightsLink service via the Permissions link on the article page on our site—for further information please contact journals.permissions@oup.com.
Conflict of interest statement
None.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Effectiveness of interventions to improve family-staff relationships in the care of people with dementia in residential aged care: a systematic review protocol.JBI Database System Rev Implement Rep. 2015 Nov;13(11):52-63. doi: 10.11124/jbisrir-2015-2415. JBI Database System Rev Implement Rep. 2015. PMID: 26657464
-
Exploration of family caregivers' experiences on coping in dementia care in Ghana: a phenomenological study.BMC Psychol. 2024 Jun 20;12(1):361. doi: 10.1186/s40359-024-01862-y. BMC Psychol. 2024. PMID: 38902797 Free PMC article.
-
The health and well-being of caregivers of children with cerebral palsy.Pediatrics. 2005 Jun;115(6):e626-36. doi: 10.1542/peds.2004-1689. Pediatrics. 2005. PMID: 15930188
-
Coping and caregivers of people with dementia.Br J Health Psychol. 2003 Feb;8(Pt 1):1-17. doi: 10.1348/135910703762879174. Br J Health Psychol. 2003. PMID: 12643813 Review.
-
The psychosocial impact of caregiving in dementia and quality of life: a systematic review and meta-synthesis of qualitative research.Psychol Health. 2018 Nov;33(11):1321-1342. doi: 10.1080/08870446.2018.1496250. Epub 2018 Sep 27. Psychol Health. 2018. PMID: 30260239
Cited by
-
Experiences of formal caregivers of elderly inpatients with physical disabilities in China: a qualitative study.BMC Nurs. 2024 Jun 7;23(1):392. doi: 10.1186/s12912-024-02019-3. BMC Nurs. 2024. PMID: 38849821 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Abdelhamid, A., Bunn, D., Copley, M., Cowap, V., Dickinson, A., Gray, L., Howe, A., Killett, A., Lee, J., Li, F., Poland, F., Potter, J., Richardson, K., Smithard, D., Fox, C., & Hooper, L. (2016). Effectiveness of interventions to directly support food and drink intake in people with dementia: Systematic review and meta-analysis. BMC Geriatrics, 16, 26. 10.1186/s12877-016-0196-3 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Braun, A., Trivedi, D. P., Dickinson, A., Hamilton, L., Goodman, C., Gage, H., Ashaye, K., Lliffe, S., & Manthorpe, J. (2019). Managing behavioural and psychological symptoms in community dwelling older people with dementia: 2. A systematic review of qualitative studies. Dementia, 18(7–8), 2950–2970. 10.1177/1471301218762856 - DOI - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous