HDAC inhibitors as pharmacological treatment for Duchenne muscular dystrophy: a discovery journey from bench to patients
- PMID: 38408879
- PMCID: PMC11095976
- DOI: 10.1016/j.molmed.2024.01.007
HDAC inhibitors as pharmacological treatment for Duchenne muscular dystrophy: a discovery journey from bench to patients
Erratum in
-
HDAC inhibitors as pharmacological treatment for Duchenne muscular dystrophy: a discovery journey from bench to patients: (Trends in Molecular Medicine, 30:3 p:278-294, 2024).Trends Mol Med. 2024 Jul;30(7):698. doi: 10.1016/j.molmed.2024.03.012. Epub 2024 Apr 19. Trends Mol Med. 2024. PMID: 38643051 No abstract available.
Abstract
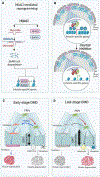
Earlier evidence that targeting the balance between histone acetyltransferases (HATs) and deacetylases (HDACs), through exposure to HDAC inhibitors (HDACis), could enhance skeletal myogenesis, prompted interest in using HDACis to promote muscle regeneration. Further identification of constitutive HDAC activation in dystrophin-deficient muscles, caused by dysregulated nitric oxide (NO) signaling, provided the rationale for HDACi-based therapeutic interventions for Duchenne muscular dystrophy (DMD). In this review, we describe the molecular, preclinical, and clinical evidence supporting the efficacy of HDACis in countering disease progression by targeting pathogenic networks of gene expression in multiple muscle-resident cell types of patients with DMD. Given that givinostat is paving the way for HDACi-based interventions in DMD, next-generation HDACis with optimized therapeutic profiles and efficacy could be also explored for synergistic combinations with other therapeutic strategies.
Keywords: HDAC inhibitors; duchenne muscular dystrophy; fibro-adipogenic degeneration; histone acetylation; muscle regeneration.
Copyright © 2024 Elsevier Ltd. All rights reserved.
Conflict of interest statement
Declaration of interests C.S. is an employee of Italfarmaco SpA. The remaining authors have no interests to declare.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Preclinical studies in the mdx mouse model of duchenne muscular dystrophy with the histone deacetylase inhibitor givinostat.Mol Med. 2013 May 20;19(1):79-87. doi: 10.2119/molmed.2013.00011. Mol Med. 2013. PMID: 23552722 Free PMC article.
-
Determinants of epigenetic resistance to HDAC inhibitors in dystrophic fibro-adipogenic progenitors.EMBO Rep. 2022 Jun 7;23(6):e54721. doi: 10.15252/embr.202254721. Epub 2022 Apr 4. EMBO Rep. 2022. PMID: 35383427 Free PMC article.
-
Histone deacetylase inhibitors: a potential epigenetic treatment for Duchenne muscular dystrophy.Epigenomics. 2014;6(5):547-60. doi: 10.2217/epi.14.36. Epigenomics. 2014. PMID: 25431946 Review.
-
Histone Deacetylases: Molecular Mechanisms and Therapeutic Implications for Muscular Dystrophies.Int J Mol Sci. 2023 Feb 21;24(5):4306. doi: 10.3390/ijms24054306. Int J Mol Sci. 2023. PMID: 36901738 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Histone deacetylase inhibitors in the treatment of muscular dystrophies: epigenetic drugs for genetic diseases.Mol Med. 2011 May-Jun;17(5-6):457-65. doi: 10.2119/molmed.2011.00049. Epub 2011 Feb 7. Mol Med. 2011. PMID: 21308150 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
The fibrosis puzzle of systemic sclerosis-associated ILD and the quest for targeted interventions.Ther Adv Respir Dis. 2025 Jan-Dec;19:17534666251366023. doi: 10.1177/17534666251366023. Epub 2025 Aug 16. Ther Adv Respir Dis. 2025. PMID: 40817801 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Harnessing traditional medicine and biomarker-driven approaches to counteract Trichostatin A-induced esophageal cancer progression.World J Gastroenterol. 2025 May 28;31(20):106443. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v31.i20.106443. World J Gastroenterol. 2025. PMID: 40495945 Free PMC article.
-
Orthopaedic Management in Duchenne Muscular Dystrophy.J Pediatr Soc North Am. 2025 Jan 2;10:100154. doi: 10.1016/j.jposna.2024.100154. eCollection 2025 Feb. J Pediatr Soc North Am. 2025. PMID: 40433579 Free PMC article. Review.
-
EZH2 inhibitor SHR2554 enhances the anti-tumor efficacy of HDAC inhibitor Chidamide through STAT1 in T-cell lymphoma.Cell Death Dis. 2025 Jul 14;16(1):522. doi: 10.1038/s41419-025-07775-x. Cell Death Dis. 2025. PMID: 40659662 Free PMC article.
-
Epigenetics-targeted drugs: current paradigms and future challenges.Signal Transduct Target Ther. 2024 Nov 26;9(1):332. doi: 10.1038/s41392-024-02039-0. Signal Transduct Target Ther. 2024. PMID: 39592582 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Brownell JE, Zhou J, Ranalli T, Kobayashi R, Edmondson DG, Roth SY, Allis CD (1996) Tetrahymena histone acetyltransferase A: A homolog to yeast Gcn5p linking histone acetylation to gene activation. Cell 84:843–851. - PubMed
-
- Mizzen CA, Yang X-Y, Kokubo T, Brownell JE, Bannister AJ, Owen-Hughes T, Workman J, Wang L, Berger SL, Kouzarides T, Nakatani Y, Allis CD (1996) The TAFII250 subunit of TFIID has histone acetyltransferase activity. Cell 87:1261–1270. - PubMed
-
- Bannister AJ, Kouzarides T. (1996) The CBP co-activator is a histone acetyltransferase. Nature 384:641–643. - PubMed
-
- Ogryzko VV, Schiltz RL, Russanova V, Howard BH, Nakatani Y. (1996) The transcriptional coactivators p300 and CBP are histone acetyltransferases. Cell 87:953–959. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

